OPM Announces 2022 FEHB and FEDVIP Premiums

OPM, as promised, announced 2022 FEHB and FEDVIP premiums before the end of September. Here are links to the OPM website for 2022 FEHB plan premiums and its website for 2022 FEDVIP plan premiums. In addition, here are links to related articles from the Washington Post, GovExec, Federal News Network, FedWeek, and the Federal Times which offered a separate article on FEDVIP.
The Washington Post summed it up as follows: “Premiums for federal employees will rise by 3.8 percent on average in 2022, the second straight year of moderate increases despite the coronavirus pandemic, the government announced Wednesday.” That’s a credit to OPM and the carriers as well as this competitive program. Also as OPM usually explains, the average increase is shown before the Open Season results when federal and postal employees and annuitants can elect lower premium plans from Nov. 8 through Dec. 13.
From Capitol Hill, the Wall Street Journal reports this evening that
Party leaders are racing to unify Democrats around changes to a separate $3.5 trillion healthcare, education and climate package, which progressives want to see advance as a condition of supporting the infrastructure bill in the narrowly divided House. Speaker Nancy Pelosi (D., Calif.) so far has stuck to her plan to bring the infrastructure bill up for a vote Thursday, saying she was taking it “one hour at a time,” though she opened the door to further delay if talks don’t progress. * * *
The Thursday deadline for the infrastructure vote is one of several scheduling crunches Democrats face in the coming days. They are also rushing to pass a stand-alone measure extending government funding, currently set to expire on Friday at 12:01 a.m., through Dec. 3. Republicans and Democrats in the Senate were nearing an agreement to pass the spending patch Thursday before sending it to the House.
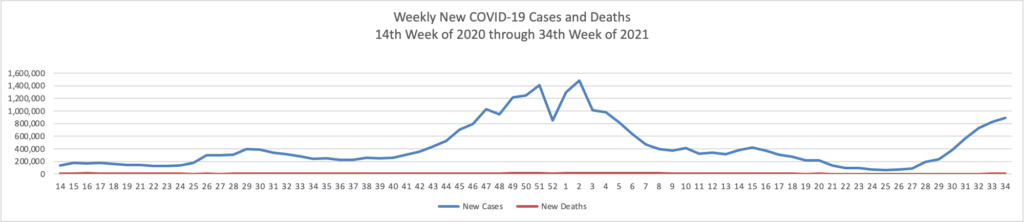
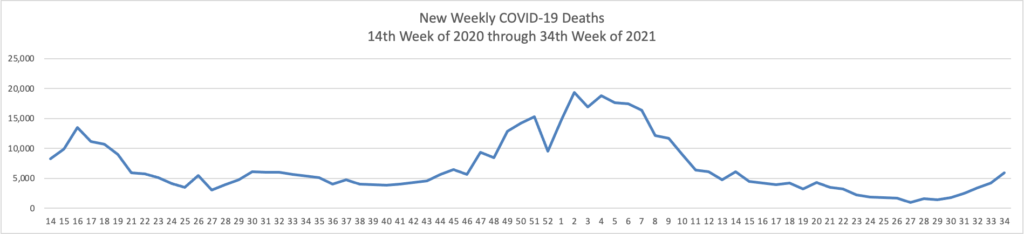
From the Delta variant front, STAT News tells us that “People who’ve received a third dose of a Covid-19 vaccine are reporting rates of side effects similar to those after the second dose, according to data released Tuesday by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.”
From the No Surprises Act front, OMB’s Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs has concluded its review of the second interim final rule which concerns the independent dispute resolution process. This means that the regulators can timely release information on the rule this week, if not the entire rule itself.
From the health equity front, Fierce Healthcare reports that “CVS Caremark is expanding its health equity efforts, setting goals that specifically target diseases that disproportionately impact patients of color, such as HIV and sickle cell disease.”
In other healthcare news
- HHS’s Agency for Healthcare Quality and Research reminds us that today is ‘World Heart Day — an observance that aims to improve how we understand, prevent, and manage the disease.” AHRQ describe its efforts to improve heart health.
- Healthcare Dive without grinding an axe informs us that
U.S. health insurance markets have become increasingly concentrated over the past half decade, according to a new report from the American Medical Association, which argues payer M&A results in rising costs and fewer care options for patients, but largely excludes the impact of provider consolidation in driving those trends.
Almost three-fourths of metropolitan statistical areas were highly concentrated in 2020 according to federal guidelines used by the Department of Justice and Federal Trade Commission, up from 71% in 2014. Of markets that were already highly concentrated in 2014, 54% become more concentrated as of last year, while 26% of markets that were not highly concentrated become so by 2020, the AMA said.
The medical association’s study is the latest salvo in a messaging war between provider and payer lobbies as they work to shift the blame for rapidly rising medical costs in the U.S.
- The National Institutes of Health reports on the efforts of its “Helping to End Addiction Long-termSM Initiative, or NIH HEAL InitiativeSM, is an aggressive, trans-agency effort to speed scientific solutions to stem the national opioid public health crisis.”