Monday Roundup

From Capitol Hill, Roll Call reports the FY 2023 National Defense Authorization Act is expected to rescind the Defense Secretary’s 2021 Covid vaccine mandate for U.S. service members. “Congressional leaders are aiming to introduce the final compromise NDAA version as soon as Tuesday, with House floor action possible later in the week.”
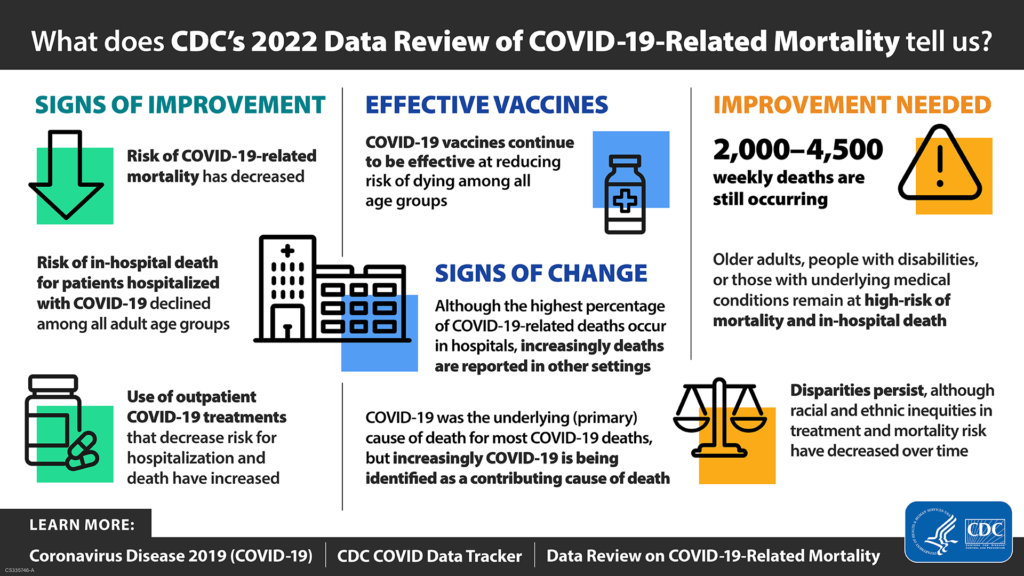
From the infectious disease front —
- Bloomberg Prognosis tells about a study confirming the Paxlovid rebounds have been blown out of proportion.
- Pfizer has asked the Food and Drug Administration for an emergency use authorization applicable to its bivalent Omicron vaccine designed for children at least six months old and not over four years old.
- The Health and Human Services Secretary has confirmed reported plans to end the mpox public health emergency when the current declaration expires at the end of January 2023. “But we won’t take our foot off the gas – we will continue to monitor the case trends closely and encourage all at-risk individuals to get a free vaccine.”
- MedPage Today interviews Demetre Daskalakis, MD, MPH, the deputy coordinator of the White House Monkeypox Response Team, about the course of the illness since it erupted in the summer
- MedPage further reports
Influenza hospitalizations this early in the season are higher than they have been in a decade, according to the CDC, with 14 pediatric deaths reported so far.
“Since October 1, there have already been at least 8.7 million illnesses, 78,000 hospitalizations, and 4,500 deaths from flu,” said CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, on a call with reporters on Monday, held in part to kick off National Influenza Vaccination Week. * * *
This year, influenza vaccines are “well matched to the viruses currently circulating,” she added. The flu shots contain protection for two influenza A and two influenza B virus strains. Of influenza A viruses detected and subtyped this season, 79% have been A(H3N2) and 21% have been A(H1N1).
The CDC recommends influenza vaccination particularly for children, immunocompromised individuals, pregnant women, and people 65 and over.
It was not clear if the pediatric deaths reported so far this season involved unvaccinated children, but Fryhofer noted that previous data showed about 80% of influenza deaths occur in unvaccinated persons.
Pregnant women who get the flu shot also protect their newborns, who are not eligible for vaccination before they are 6 months of age, Fryhofer said. “If you’re not doing it for you, do it for your baby.”
- For context, here are the flu case and death statistics from the last flu season before Covid struck, October 2019 through March 2020.
| 2019 – 2020 Winter CDC Fluview | 3/28/20 |
| Flu Deaths | 24,000 |
| Flu Cases | 39,000,000 |
The flu is a highly contagious, dangerous disease.
- NPR Shots offers consumer advice should they counter pharmacy shelves with a low or no supply of anti-fever drugs.
From the telehealth front, Health Leaders Media tells us
According to a survey commissioned by America’s Health Insurance Plans, almost 70% used telehealth in the past year because it’s more convenient than in-person care, and almost 80% say telehealth makes it easier to seek out care.
Almost 50% used telehealth because they were unable to make an in-person appointment, while 24% said they wanted to save money.
Some 36% used telehealth just once over the past year, while 53% used it between two and five times.
From the mental healthcare front, Health Payer Intelligence reports
CareFirst BlueCross BlueShield (CareFirst) is providing community-based organizations with nearly $8 million in grants to help improve behavioral healthcare access and quality for underserved youth.
The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated the mental and behavioral health crisis among children, adolescents, and families. In response, CareFirst is investing in 19 community-based organizations in Maryland, Washington, DC, and Northern Virginia.
“CareFirst recognizes that behavioral health is an essential part of overall health, which includes a continuum of conditions ranging from severe mental health disorders to the emotional, psychological, and social factors that affect a person’s overall wellbeing,” Destiny-Simone Ramjohn, PhD, vice president of community health and social impact at CareFirst, said in the press release.
Kudos
From the Rx coverage front, Fierce Healthcare informs us
Express Scripts, which is part of Cigna’s Evernorth subsidiary, said Monday that it will add biosimilars for Humira to its largest formularies as preferred products available for patients with inflammatory conditions. Like other major PBMs, Express Scripts sees significant potential in biosimilars to help address the massive costs associated with specialty drugs.
Specialty drugs account for just 2% of prescriptions but drive half of drug spending.
In October 2021, Express Scripts announced that it would put Semglee, the first Food and Drug Administration-approved interchangeable insulin biosimilar, on its National Preferred Formulary for 2022. The company estimates that this move generated $20 million in savings in the first year.
From the federal government employee benefits front, Federal News Network relates
The Office of Personnel Management plans to suspend applications for the Federal Long Term Care Insurance Program for two years beginning Dec. 19, in anticipation of a sizeable rate hike.
OPM announced the unusual measure last month in the Federal Register, and noted that federal workers who submit their applications by the deadline will still be considered for enrollment. FLTCIP was created in 2002 and assists with health care costs for participants who need help with daily personal functions, or who have a severe cognitive illness, and covers home care, nursing home or assisted living benefits.
“OPM is suspending applications for coverage in FLTCIP to allow OPM and the FLTCIP carrier to assess the benefit offerings and establish sustainable premium rates that reasonably and equitably reflect the cost of the benefits provided,” the agency wrote.
The program will continue to operate normally for current enrollees, although they will not be able to apply to increase their coverage. There are currently around 267,000 federal workers and retirees participating in the insurance plan, and OPM typically receives only a few thousand applications to enroll per year.
The decision to suspend applications for the program came after John Hancock Life and Health Insurance Co., the contractor that administers the program, informed OPM that it is likely that there will a premium increase sometime next year.
Finally, the Wall Street Journal offers an interesting article about medical research that is “uncovering links between your ‘subjective age’ [as opposed to your chronological age] and your future health and longevity.”