Midweek update

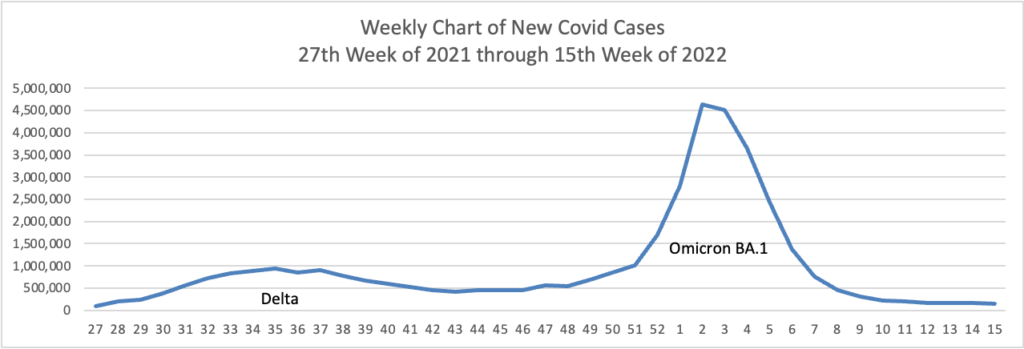
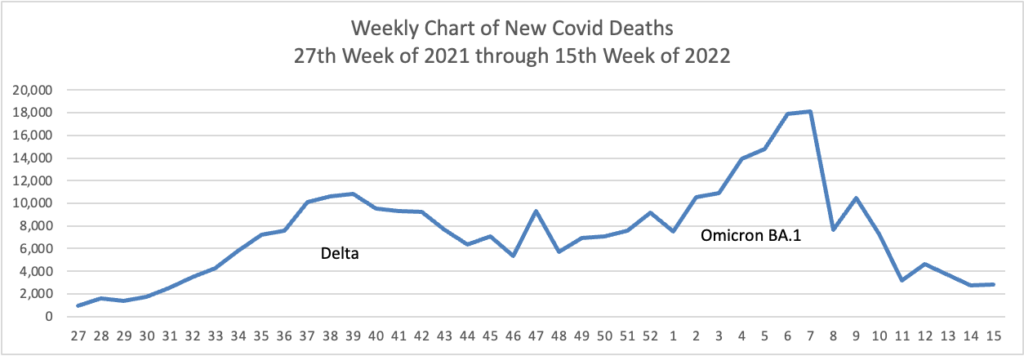
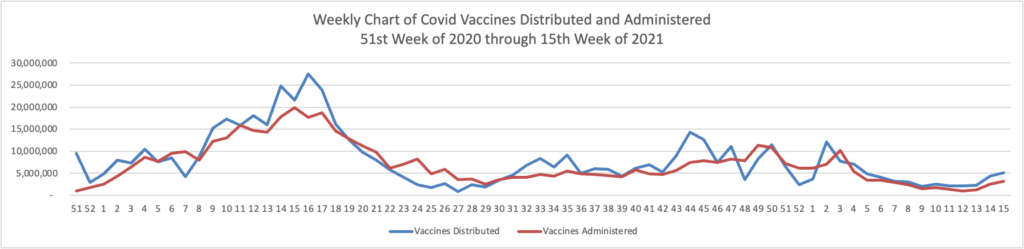
From the Omicron and siblings front
The American Hospital Association informs us
COVID-19 vaccinations prevented an estimated 107,000 Medicare hospitalizations between January and May 2021, resulting in $2.6 billion in savings for Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans, according to a new report by the Department of Health and Human Services. The report estimates the impact of COVID-19 vaccination during a five-month period shortly after the first vaccine was authorized and recommended for health care workers and elderly people in long-term care facilities. Future analyses will examine hospitalizations prevented by vaccination during the delta and omicron waves, HHS said.
Bloomberg Prognosis tells us
Pfizer Inc. executives said patients who suffer a relapse in Covid-19 symptoms after taking a full course of Paxlovid should take more of the treatment, though current U.S. guidelines limit use to five consecutive days.
“Paxlovid does what it has to do: it reduces the viral load,” Chief Executive Officer Albert Bourla said in an interview. “Then your body is supposed to do the job.” But for unknown reasons, the CEO said, some patients aren’t able to clear the virus with the first course of treatment.
In cases where virus levels do rebound, Bourla said, “then you give a second course, like you do with antibiotics, and that’s it.”
As noted in the article, the fly in the ointment is that the FDA emergency use authorization does not expressly approve a second course of the medication.
From the Rx coverage front
MedCity News reports on Bristol Myers Squibb’s (BMS) NEX-T program to improve CAR-T treatments.
The company has described NEX-T as changes to manufacturing driven by the translational insights it has gleaned from treating thousands of patients with its CAR T therapies. In addition to a faster turnaround time, the strategy is intended to reduce the costs of the overall process.
One of the key goals for the next-generation of cell therapies is treating solid tumors.
Another strategy that BMS is pursuing is going after two targets with a single therapy, reducing the risk that a tumor escapes from the treatment
Looking at the flip side of this coin, Forbes reports
Health plans and pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) that manage drug costs speaking at this year’s Asembia Specialty Pharmacy Summit in Las Vegas say specialty drugs now account for 50% or greater of the total prescription spending they manage. In some cases, employer clients are seeing specialty costs account for 60% or even greater of their total drug spending.
“It really is frightening for our clients,” Lucille Accetta, senior vice president of pharmacy benefit management and specialty product development at CVS Health told hundreds of attendees at the Asembia event, which runs through Thursday and drew more than 5,000 people from the healthcare industry. “We have to be the best purchaser for our clients.” * * *
To reign in the costs of prescription drugs while maintaining access to life-saving treatments, health plans and pharmacies say they are more closely monitoring patients as soon as they are on the drug, said Rina Shah, group vice president of pharmacy operations and services at Walgreens.
The Forbes article adds
Abarca Health [is] an independent PBM that manages more than $5 billion in drug costs annually for more than four million Americans has executives at this week’s Asembia meeting talking up its efforts to better manage specialty pharmacy costs.
The company’s Assura solution launched earlier this year “guarantees the net cost of drugs, including specialty medications, by offering an annual fixed per script cost for a health plan’s entire population,” Abarca said in announcing the new pricing solution earlier this year. The guarantee, Abarca CEO Jason Borschow says, is adjusted each year based on drug benefit coverage changes.
From the healthcare business front
Healthcare Dive informs us
Even as COVID-19’s benefit waned, new plan members across multiple product lines helped drive CVS to $2.3 billion in profit in the first quarter, slightly higher than the $2.2 billion brought in at the same time last year.
In results published Wednesday, the company beat Wall Street expectations on earnings and revenue, with a topline of $76.8 billion, up 11% year over year.
Fierce Healthcare explains how CVS has shifted from a retail to a digital marketing focus.
The Wall Street Journal reports
Moderna Inc. MRNA 5.81% said that its first-quarter revenue and profit tripled from a year earlier on higher sales of its Covid-19 vaccine and that a fall booster-shot campaign could drive continued sales gains.
The biotechnology company’s revenue topped $6 billion in the period ended March 31, beating analyst expectations and rising from $1.94 billion a year earlier, driven almost entirely by sales of its messenger RN
Moderna Inc. MRNA 5.81% said that its first-quarter revenue and profit tripled from a year earlier on higher sales of its Covid-19 vaccine and that a fall booster-shot campaign could drive continued sales gains.
The biotechnology company’s revenue topped $6 billion in the period ended March 31, beating analyst expectations and rising from $1.94 billion a year earlier, driven almost entirely by sales of its messenger RNA-based vaccine, branded as Spikevax. * * *
Moderna is the latest drugmaker to show surging sales due to demand for Covid-19 vaccines and treatments, following recent reports fromEli Lilly & Co., Merck & Co. and Pfizer Inc.
From the health risks front, MedPage Today explains that
Seven risk factors, some modifiable and some not, accounted for the vast majority of risk for first-time acute myocardial infarction (MI) in young adults, according to a case-control study.
The seven factors — diabetes, depression, hypertension, smoking, family history of premature MI, low household income, and hypercholesterolemia — were responsible for 83.9% of the total acute MI risk in young women and 85.1% of the risk in young men, reported Harlan Krumholz, MD, SM, of Yale New Haven Hospital in New Haven, Connecticut, and colleagues.
The UPI reports
Older adults who obtain a flu shot are less likely to suffer a heart attack or stroke and are at lower risk for death from heart-related health events in the year after getting vaccinated, an analysis published Friday found.
Just under 4% of older adults vaccinated against the seasonal virus experienced a “cardiovascular event” within the next year compared to just over 5% of those who did not receive the shot, data published Friday by JAMA Network Open showed.
From the meetings department,
- HHS provides a readout of a high-level meeting among Labor Department, health insurance and business executives “to discuss compliance with the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act, adequacy of in-network providers and mental health and substance use disorder treatment during the pandemic, as the nation observes Mental Health Awareness Month.”
- The National Committee for Quality Assurance reviews the presentations at last week’s Quality Talks conference.
From the federal employee benefits front, FedWeek discusses OPM’s planned improvement to processing retirement applications as unveiled in the Fiscal Year 2023 budget document. Processing federal retirement benefits will be a heavy lift for OPM until Congress simplifies the pension calculation.