Friday Stats and More
Based on the Centers for Disease Control’s COVID-19 Data Tracker website, here is the FEHBlog’s chart of new weekly COVID-19 cases and deaths over the 14th week of 2020 through 31st week of this year (beginning April 2, 2020, and ending August 4, 2021; using Thursday as the first day of the week in order to facilitate this weekly update):
and here is the CDC’s latest overall weekly hospitalization rate chart for COVID-19:

The FEHBlog has noticed that the new cases and deaths chart shows a flat line for new weekly deaths because new cases significantly exceed new deaths. Accordingly here is a chart of new COVID-19 deaths over the period (April 2, 2020, through August 4, 2021):
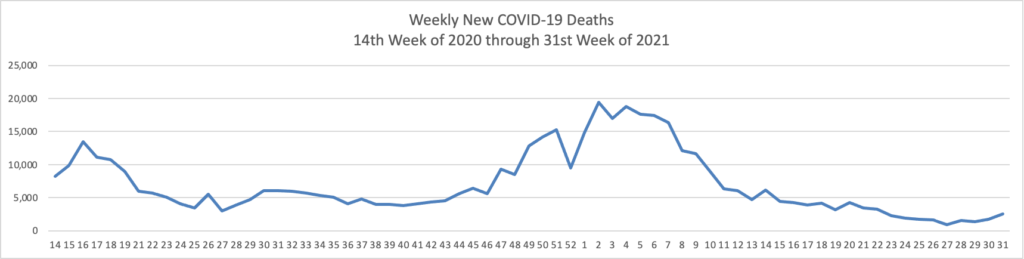
Finally here is a COVID-19 vaccinations chart over the period December 17, 2020, through August 24, 2021, which also uses Thursday as the first day of the week:
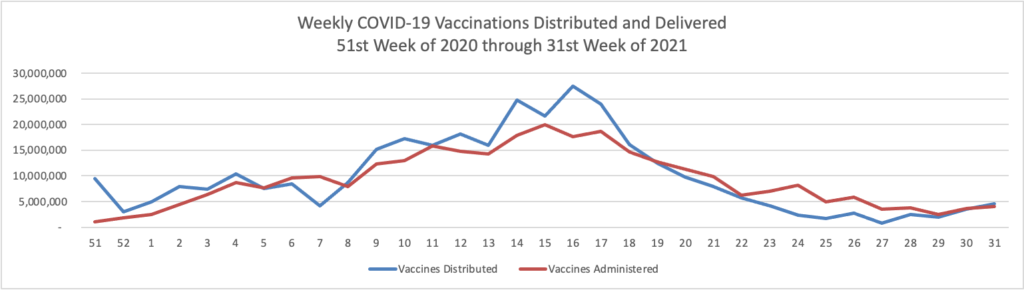
While COVID-19 cases are soaring, the number of deaths remains stable thanks to the high vaccination rates for Americans over age 65. It is also encouraging that the number of administered vaccinations also is increasing.
In other Delta variant news:
- Surprisingly, according to STAT News, “with nearly 20% of all U.S. Covid cases last week recorded in children, the American Academy of Pediatrics and 11 other organizations put out a consensus statement this week calling on providers conducting sports physicals to ask about children’s Covid vaccination status and to use it as an opportunity to administer a vaccine, if possible.”
- Fierce Pharma tells us that “In a trial of nearly 480,000 healthcare workers in South Africa, Johnson & Johnson‘s one-dose vaccine helped prevent severe disease from the Delta variant, Bloomberg reports. The trial is the first piece of large-scale evidence that shows the shot works against the variant, the news service stated. In fact, Glenda Gray, one of the leaders of the work, said the vaccine may provide better protection against Delta than the Beta variant.”
- MedPage Today reports that “Unvaccinated adults who were previously infected with COVID-19 were twice as likely to be reinfected as those previously infected but also fully vaccinated, researchers found. A case-control study in Kentucky found a more than two times higher risk of COVID-19 cases among unvaccinated adults with prior infection compared with their fully vaccinated counterparts (OR 2.34, 95% CI 1.58-3.47), reported Alyson Cavanaugh, PhD, of the CDC, and colleagues, writing in an early edition of the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.“
- In related news Precision Vaccines tells us that “The World Health Organization (WHO) issued Influenza Update N° 399 on August 2, 2021, saying, ‘Globally, despite continued or even increased testing for influenza in some countries, influenza activity remained at lower levels than expected for this time of the year.'”
From the No Surprises Act (“NSA”) front, the FEHBlog discovered today that last Tuesday the tri-agencies and OPM submitted their second NSA interim final rule, which concerns the independent dispute resolution process, to OMB’s Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs for final review. OIRA already has two listening sessions concerning this rule making on its calendar. This indicates that the second interim final rule will be made public in early September, rather than on its October 1, 2021, due date.
From the federal employee front
- Govexec brings us up to date on the development of the President’s mandatory vaccination program for federal employees. “The Safer Federal Workforce Task Force—a group President Biden created by executive order that is led by the White House, General Services Administration and Office of Management and Budget—confirmed in new guidance agencies would not initially ask for proof of vaccination, but they could follow up for documentation if they receive “a good faith allegation that strongly suggests” an employee lied on their attestation form. Those “certification of vaccination” forms will soon go out via email to all federal employees, with an Office of Management and Budget official saying that process will begin next week. While agencies will initially rely on the honor system as it begins asking employees for their vaccination status, the administration made clear there could be consequences for lying.”
- Govexec also discusses how Medicare Advantage plans are being integrated into FEHB plans. The trend started with HMOs and the APWU Health Plan picked it up for this year. Expect more plans to follow suit for 2022.
In more news
- Earlier this week, the FEHBlog noted a Reuters report that the Justice Department is preparing to file suit to block Optum’s acquisition of Change Healthcare. Fierce Healthcare reports today au contraire that “Change Healthcare President and CEO Neil de Crescenzo said Thursday he’s pleased with the company’s progress on regulatory review of its pending deal with Optum and is moving forward with plans for a successful integration. ‘We look forward to continuing to work diligently in coordination with UHG (UnitedHealth Group) to provide the necessary information requested by the DOJ (Department of Justice) and completing the transaction.'” Time will tell.
- Medcity News informs us that “GoodRx struck a partnership with medication data giant Surescripts that would let healthcare providers access cash price information on medications. Arlington, Virginia-based Surescripts dominates the e-prescribing market, offering technology that routes clinicians’ electronic prescriptions directly to pharmacies. It’s owned by CVS Health and Express Scripts, and nearly 2 billion prescriptions were delivered through its software last year.”
- mHealth Intelligence tells us that “While the pandemic prompted an unprecedented surge in telehealth to address healthcare needs, it also highlighted the gap between those who can access care and those who can’t. Now health systems, community health organizations, non-profits and philanthropic groups are moving to address those gaps with programs that use telehealth to extend care to those who can’t access or afford it. They’re fueling a surge in connected health charities and projects targeting the social determinants of health. Among those groups is Beam Up, an organization launched by telehealth company Beam Healthcare to address gaps in access to health food, quality education and healthcare services. Executives see a need for these services not only in other countries – a partnership with Tyto Care is equipping a handful of orphanages in Mexico with telemedicine technology – but in cities and rural regions across the United States.





