Tuesday’s Tidbits

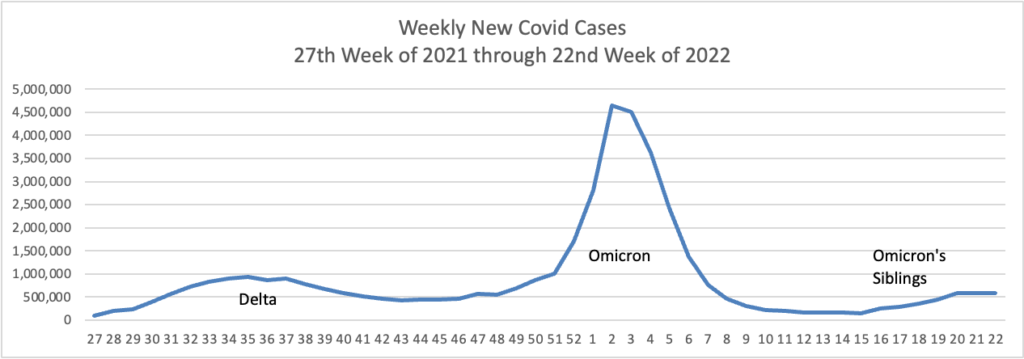
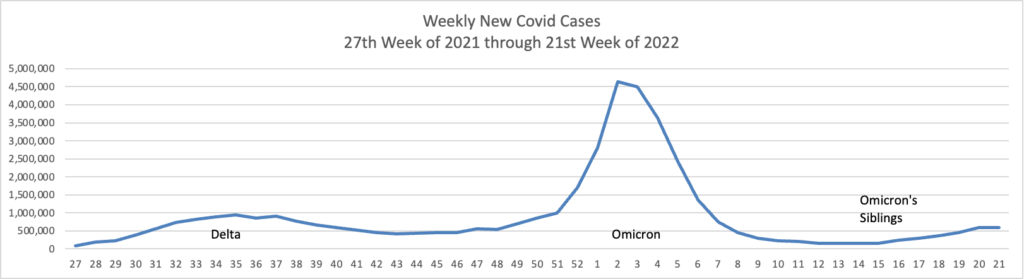
From the Omicron and siblings front, the Wall Street Journal reports
Omicron Covid-19 variants BA.4 and BA.5 are on the rise in the U.S., adding two more highly contagious versions of the virus to the mix that has fueled a springtime surge in cases.
The closely related subvariants represented a combined 13% of U.S. cases for the week ended June 4, according to estimates the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released on Tuesday. Evidence suggests the variants are yet-more contagious versions of Omicron, public-health experts said, that may be able to evade some of the immune protections people built up from infections triggered by another version of Omicron during the winter.
The spread of the subvariants could at least prolong the time it takes to emerge from the current wave fueled by other versions of Omicron, some health experts said.
The Journal adds
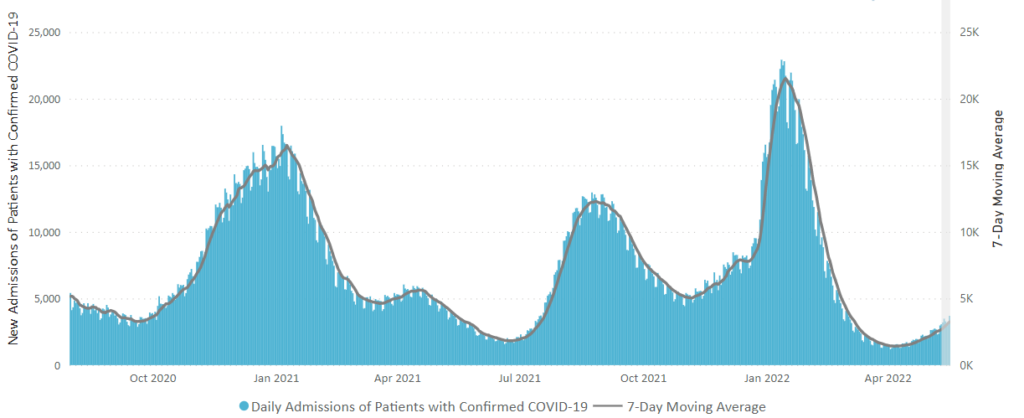
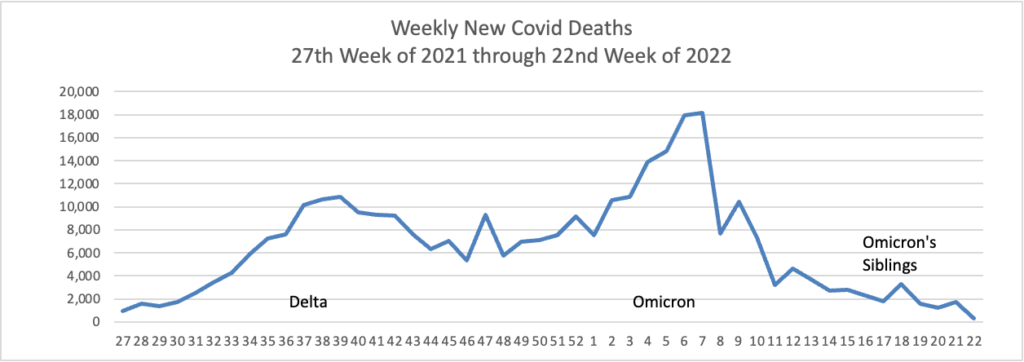
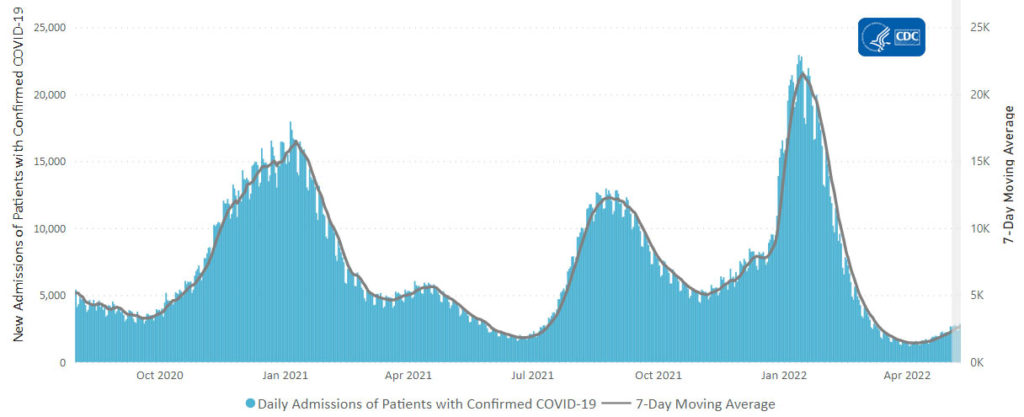
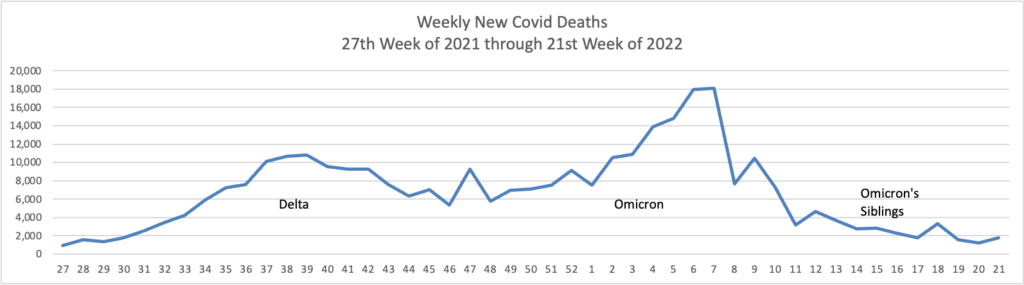
This case wave hasn’t translated to a significant surge in severe illness. Hospitalizations, while up, remain far below earlier peaks, and reported Covid-19 deaths have recently hovered near historically low levels. * * * Epidemiologists believe built-up immunity from vaccines and prior infections have bolstered defenses against severe illness, even though many people are falling ill from both breakthrough and repeat infections.
AHIP informs us
Today the Food and Drug Administration’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) recommended that the FDA grant emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Novavax COVID-19 vaccine in adults by a vote of 21-0.
The Committee reviewed data from Novavax showing that the benefits of the two-dose primary series outweigh the potential risks. The Committee noted the importance of making a vaccine available that has an alternative method of action, different from the mRNA vaccines currently available in the U.S., in the hope that a more traditional vaccine may appeal to those currently unvaccinated and those who may have an allergy to the components of the mRNA vaccines.
Committee members agreed that the FDA should come to an agreement with Novavax on how the company will identify and evaluate a possible causal link between its vaccine and cases of heart inflammation, though the company has argued there’s not yet enough evidence to establish a definitive link. The FDA is expected to make a decision on granting Novavax an EUA soon, whereby the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) will meet to determine when and how the vaccine should be administered.
BioPharma Dive tells us
Pfizer on Monday announced plans to invest $120 million in a drug manufacturing facility located in Kalamazoo, Michigan, which will lead to the creation of over 250 jobs.
The investment is aimed at accelerating production of Pfizer’s COVID-19 pill Paxlovid, demand for which has risen after Pfizer’s initial struggles to make sufficient quantities following the drug’s clearance in December. To date, Pfizer has delivered 12 million courses of the drug across 37 countries, 5 million of which have been shipped to the U.S.
The Kalamazoo plant, one of Pfizer’s largest drugmaking sites, will make the starting materials and active ingredient contained within Paxlovid. The new investment expands the site’s capacity, making it one of the world’s largest producers of pharmaceutical ingredients, according to Pfizer.
From the Rx coverage front, the Federal Trade Commission announced
The Federal Trade Commission announced today that it will launch an inquiry into the prescription drug middleman industry, requiring the six largest pharmacy benefit managers to provide information and records regarding their business practices. The agency’s inquiry will scrutinize the impact of vertically integrated pharmacy benefit managers on the access and affordability of prescription drugs. As part of this inquiry, the FTC will send compulsory orders to CVS Caremark; Express Scripts, Inc.; OptumRx, Inc.; Humana Inc.; Prime Therapeutics LLC; and MedImpact Healthcare Systems, Inc. * * *
The inquiry is aimed at shedding light on several practices that have drawn scrutiny in recent years including:
** fees and clawbacks charged to unaffiliated pharmacies;
** methods to steer patients towards pharmacy benefit manager-owned pharmacies;
** potentially unfair audits of independent pharmacies;
** complicated and opaque methods to determine pharmacy reimbursement;
the prevalence of prior authorizations and other administrative restrictions;
** the use of specialty drug lists and surrounding specialty drug policies;
** the impact of rebates and fees from drug manufacturers on formulary design and the costs of prescription drugs to payers and patients.
The Commisioners voted 5-0 to commence the investigation. Responses from the PBMs to the FTC’s compulsory orders are due in 90 days.
From the Pride Month front, Health Payer Intelligence reports “Members of the LGBTQ+ community reported varying experiences of discrimination in the health insurance industry but indicated that payer health equity may be improving, according to a survey from Healthcare.com.” Survey details are available in the article and the survey.
From the miscellany department
- The American Medical Association offers expert guidance on understanding blood pressure readings.
- The Centers for Disease Control explains the connection between diabetes and the brain.
- Fierce Healthcare informs us that
Anthem has partnered with Happify Health to offer a slate of new digital tools for women’s health.
Happify’s platform is based on “sequences,” or digital experiences that it uses to support specific medical conditions. These sequences combine evidence-based digital therapeutics, online communities, coaching and tailored local resources in one unified platform.
Happify’s sequences are able to integrate with existing systems and solutions for ease of navigation, according to the announcement.
- AHIP tells us
Everyone deserves access to mental health support that is effective and affordable. With more Americans than ever seeking help for mental health concerns, AHIP conducted a nationwide survey to understand people’s experience accessing care, whether their treatment was covered by insurance, and if insured patients were satisfied with the results. The findings reveal that nearly all respondents who sought mental health care for themselves or someone within their household over the past 2 years received treatment, and 3 in 4 insured Americans (73%) found it easy to get the care they needed. More than two-thirds of respondents were able to find an appointment with a provider in less than a month. In addition, 9 in 10 reported being satisfied with the mental health support they received, including half who say they were very satisfied.