Monday Roundup

From Capitol Hill, Roll Call reports
Senate negotiators have reached agreement on a $10 billion pandemic relief package that includes funding for domestic needs but not international aid, according to two Senate aides who were not authorized to speak publicly.
The deal crystallizes an informal “agreement in principle” the parties reached last week to provide $10 billion for near-term pandemic needs by repurposing unspent funds from prior relief laws.
The Wall Street Journal adds
The White House backed the deal and urged Congress to pass the bill promptly, while noting it was less than the $22.5 billion the administration had requested for vaccines, boosters, treatments and testing.
“We will continue to work with Congress to fund our remaining domestic needs,” said Press Secretary Jen Psaki in a statement. She added that the White House would continue to press for funding global vaccination efforts.
The FEHBlog noticed that the Senate Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs Committee held a business meeting last Wednesday. The Committee favorably reported the President’s nomination of Kristin Boyd to be OPM Inspector General by voice vote (with Sen. Hawley (R Mo.) voting no). The next step for Ms. Boyd’s nomination is the Senate floor.
Last week, the House of Representatives passed a Secure 2.0 bill applicable to private sector defined contribution plans. The Senate is likely to approve the bill too. The Society for Human Resource Management has reviewed the bill’s provisions.
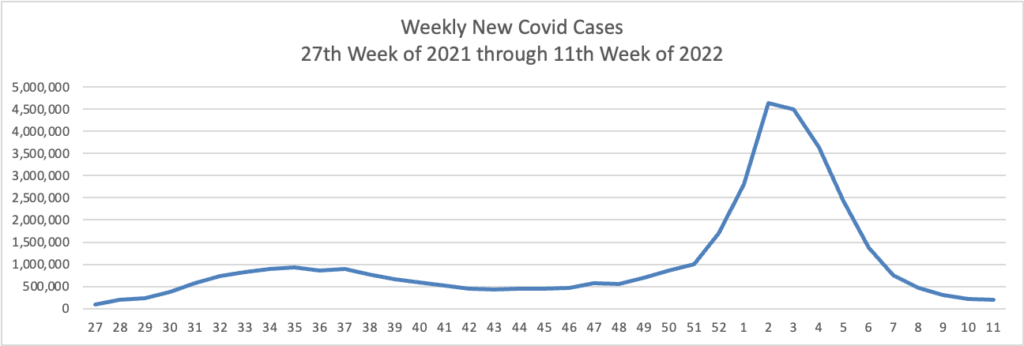
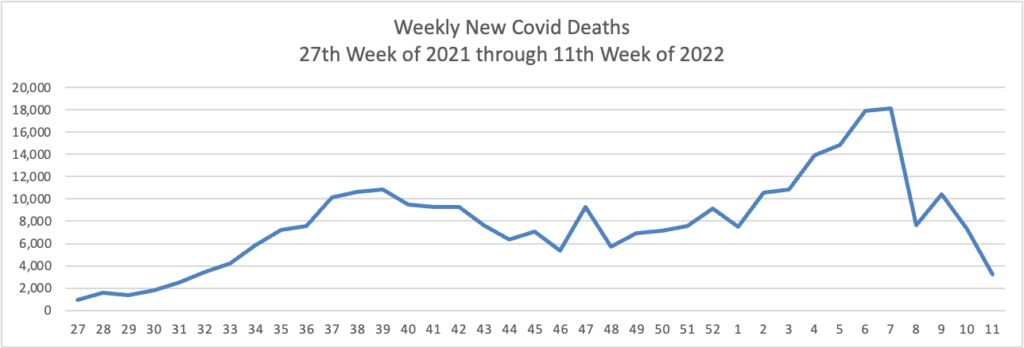
From the Omicron and siblings front —
- Becker’s Hospital Review informs us “The World Health Organization is monitoring a new omicron variant — dubbed XE — that’s a hybrid of BA.1, the original omicron strain, and BA.2, a highly transmissible subvariant.” The hybrid is estimated to be 10% more contagious that BA.2.
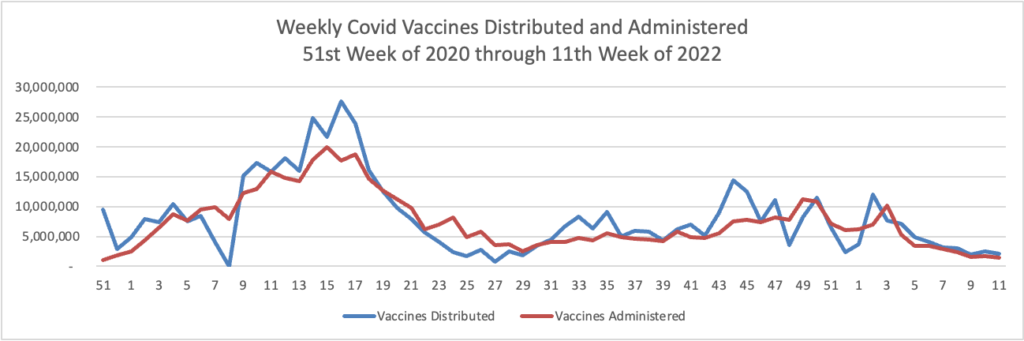
- American Hospital Association tells us “Beginning today through the end of the public health emergency, Medicare Part B beneficiaries may obtain up to eight free over-the-counter COVID-19 tests per month through eligible health care providers and pharmacies, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services announced.” Medicare Part B beneficiaries can obtain the free tests by showing their Medicare identification card.
- The American Medical Association discusses “How we will know when COVID-19 has become endemic.” The FEHBlog tends to think that we are there.
- The Centers for Disease Control announced
The new nationwide Test to Treat initiative provides quick access to free treatment for COVID-19. Through this program, people can get tested and – if they are positive and treatments are appropriate for them – receive a prescription from a health care provider, and have their prescription filled all at one location.
These “One-Stop Test to Treat” sites are available at hundreds of locations nationwide, including pharmacy-based clinics, federally qualified health centers, and long-term care facilities.
People can continue to be tested and treated by their own health care providers who can appropriately prescribe these oral antivirals at locations where the medicines are distributed.
A call center 1-800-232-0233 is available every day from 8:00 am to midnight ET to get help in more than 150 other languages.
The Disability Information and Access Line is available to help people with disabilities access services. Call 1-888-677-1199, Monday-Friday from 9:00 am to 8:00 pm ET or email DIAL@usaginganddisability.org.
From the CMS front, the agency announced that “the updated MMSEA Section 111 GHP User Guide version 6.5 has been posted to the GHP User Guide page on CMS.gov. Refer to Chapter 1 for a summary of updates.” Section 111 is a system that has been in place for about 12 years. Section 111 helps CMS keep tabs on Medicare beneficiaries and beneficiaries using data group health plans, including FEHB plans, automobile and liability insurers, and attorneys for injured Medicare beneficiaries.
CMS also released “the Announcement of Calendar Year (CY) 2023 Medicare Advantage (MA) Capitation Rates and Part C and Part D Payment Policies (the Rate Announcement).”
From the healthcare conference front, Fierce Healthcare tells us about the 2022 Health Datapalooza and National Health Policy Conference being held today and tomorrow in Arlington, VA.
From the federal employment front, Govexec reports
Federal employees can hold elected partisan office while also working at their agencies, a key panel found in a ruling setting a new precedent for civil servants.
Rodney Cowan did not have to give up his role as a county commissioner in Tennessee or be removed from his job with the U.S. Postal Service, the recently reconstituted central body of the Merit Systems Protection Board said in a decision last week. It was one of the first decisions of MSPB’s central board as it addresses its backlog of more than 3,500 cases that have piled up during its five years without a quorum.
The FEHBlog doubts that we have heard the last word on this issue.