Friday Stats and More
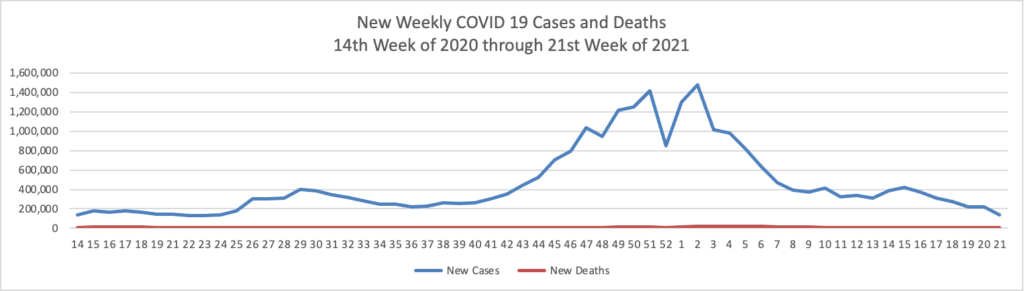
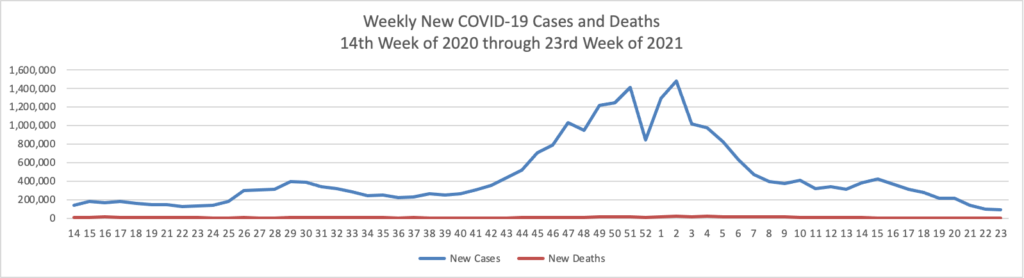
Based on the Centers for Disease Control’s COVID-19 Data Tracker website, here is the FEHBlog’s chart of new weekly COVID-19 cases and deaths over the 14th week of 2020 through 23rd week of this year (beginning April 2, 2020, and ending June 9, 2021; using Thursday as the first day of the week in order to facilitate this weekly update):
and here is the CDC’s latest overall weekly hospitalization rate chart for COVID-19:

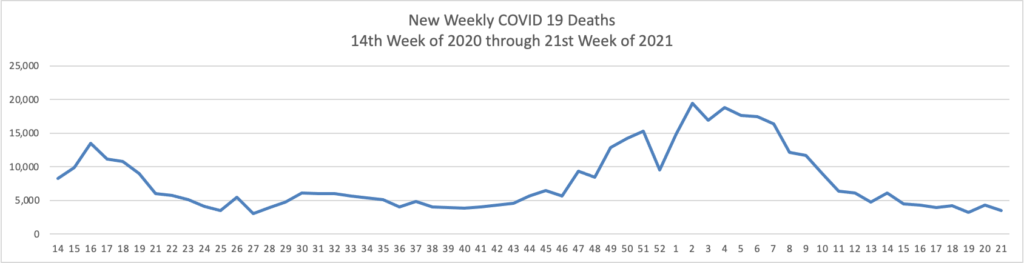
The FEHBlog has noticed that the new cases and deaths chart shows a flat line for new weekly deaths because new cases significantly exceed new deaths. Accordingly here is a chart of new COVID-19 deaths over the period (April 2, 2020, through June 9, 2020):
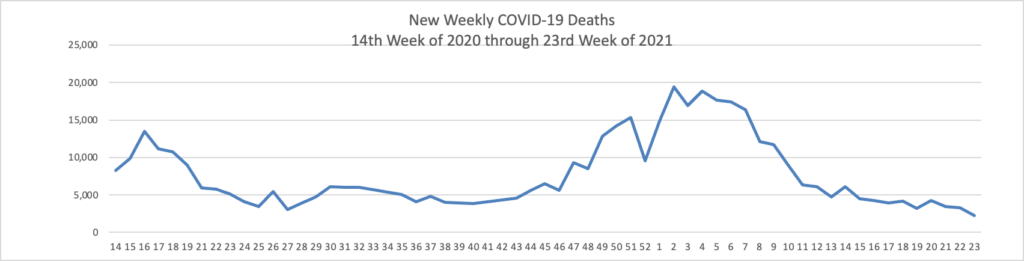
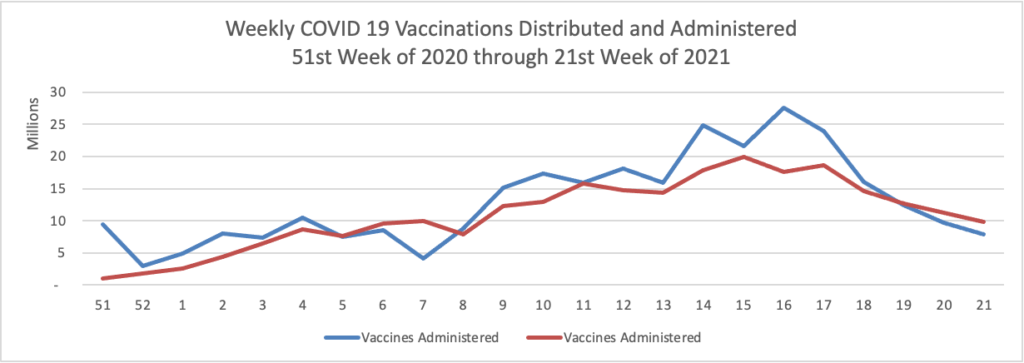
Finally here is a COVID-19 vaccinations chart over the period December 17, 2020, through June 9, 2021, which also uses Thursday as the first day of the week:
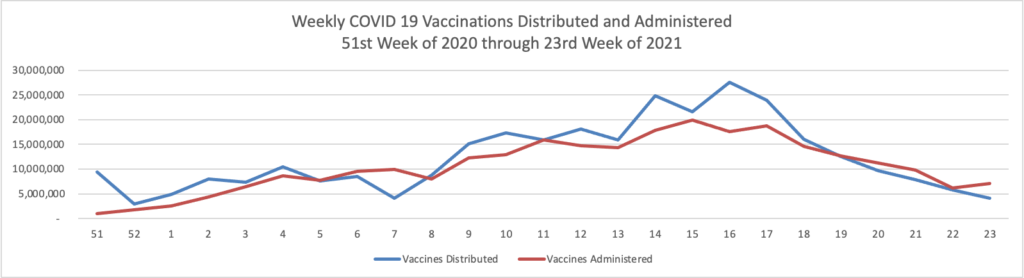
All signs continue to look up. 50% of the American population over 12 years old is fully vaccinated per the CDC.
In COVID-19 news, the Food and Drug Administration announced the latest actions stemming from its ongoing investigation of the problematic Emergent Biosolutions Baltimore factory that had been manufacturing the Johnson & Johnson one dose COVID-19 vaccine:
[The FDA] is authorizing for use, under the emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine, two batches of vaccine drug substance manufactured at the Emergent BioSolutions facility in Baltimore. Before making this decision, the FDA conducted a thorough review of facility records and the results of quality testing performed by the manufacturer. Based on this review and considering the current COVID-19 public health emergency, the FDA concluded these batches are suitable for use. While the FDA is not yet ready to include the Emergent BioSolutions plant in the Janssen EUA as an authorized manufacturing facility, the agency continues to work through issues there with Janssen and Emergent BioSolutions management. * * *
The FDA has determined several other batches are not suitable for use, but additional batches are still under review and the agency will keep the public informed as those reviews are completed.
Per Fierce Healthcare, the New York Times is reporting that the unsuitable batches total 60 million vaccine doses. Yikes.
HR DIve reports
Most employers “no longer need to take steps to protect their workers from COVID-19 exposure in any workplace, or well-defined portions of a workplace, where all employees are fully vaccinated,” the Occupational Safety and Health Administration said in guidance updated Thursday.
The agency also published an emergency temporary standard for U.S. healthcare employers. Employers included in the emergency temporary standard’s definition must develop and implement a plan to protect employees from COVID-19 in the workplace, and they must designate one or more workplace COVID-19 safety coordinators to implement and monitor their plans. The document also lays out requirements for patient screening and management, personal protective equipment and physical distancing, among other subjects.
OSHA’s updated guidance for all industries, meanwhile, encourages employers to grant paid time off for employees to get vaccinated. Employers also should implement physical distancing for unvaccinated and other at-risk workers in communal work areas, including limiting the number of such workers in one place at any given time.
In other healthcare news
- Precision Vaccines informs us about an Avalere Heath study finding that non-COVID immunizations among adolescents and adults were significant down last year.
- The American Medical Association discusses five ways healthcare must change for the post-pandemic world.
- Becker’s Hospital Review tells us that
Cleveland Clinic, IBM, Aetna and Anthem have partnered to form a blockchain health firm, called Avaneer Health.
The Chicago-based healthcare company will aim to use blockchain capabilities to make healthcare more efficient and reduce administrative costs, according to a June 9 news release.
Five things to know:
Avaneer Health will be formed as a standalone business with significant investments from its founders: Aetna, Anthem, Cleveland Clinic, Health Care Service Corporation, IBM, The PNC Financial Services and Norfolk, Va.-based Sentara Healthcare.
Avaneer Health is a member-based open network supporting utilities developed for the healthcare industry. It is expected to improve healthcare by removing administrative barriers and alleviate inefficiencies in cross-party transactions that slow down care delivery.
The incoming CEO will be Stuart Hanson, former managing director and senior healthcare industry executive at JPMorgan Chase. He will take the helm in August.
The company will be built on blockchain technology to ensure privacy and reduce costs of data exchange.
Finally, the Biden Administration released its Spring 2021 semi-annual regulatory agenda.
The Unified Agenda provides uniform reporting of data on regulatory and deregulatory activities under development throughout the Federal Government, covering approximately 60 departments, agencies, and commissions. Each edition of the Unified Agenda includes regulatory agendas from all Federal entities that currently have regulations under development or review. Agencies of the United States Congress are not included. Fall editions of the Unified Agenda include The The Regulatory Plan, which presents agency statements of regulatory priorities and additional information about the most significant regulatory activities planned for the coming year.
The FEHBlog will be discussing the OPM agenda in next week’s posts.
In this week’s Econtalk podcast episode, the host Russ Roberts holds a conversation with author Ian Leslie about his book Conflicted. “Leslie argues that, far from being a negative thing, conflict is often the essential ingredient that helps us get to the right answer or best solution. Because some of our best thinking comes in collaboration with others, learning how to disagree civilly when our views conflict is the key to productive conversation in business and in marriage.” Outstanding.