Weekend update

Congressional election day is Tuesday. The lame duck session will be next Monday.
Also next Monday, the Federal Employee Benefit Open Season will kick off. OPM has made the 2023 FEHBP and FEDVIP plan comparison tools available. Check them out.
Govexec reports on OPM Director Kiran Ahuja’s speech last Wednesday Wednesday at the annual meeting of the National Academy of Public Administration.” Ms. Ahuja said “the federal government’s HR agency is hard at work finding ways to improve the federal government’s personnel systems and shifting toward becoming a modern leader on strategic human capital issues.”
From the Rx coverage front, NPR Shots tells us
If you were prescribed medicine to lower your risk of a heart attack or stroke, would you take it?
Millions of Americans are prescribed statins such as Lipitor, Crestor or generic formulations to lower their cholesterol. But lots of people are hesitant to start the medication.
Some people fret over potential side effects such as leg cramps, which may be – or may not be – linked to the drug. As an alternative, dietary supplements, often marketed to promote heart health, including fish oil and other omega-3 supplements (Omega-3’s are essential fatty acids found in fish and flaxseed), are growing in popularity.
So, which is most effective? Researchers at the Cleveland Clinic set out to answer this question by comparing statins to supplements in a clinical trial. They tracked the outcomes of 190 adults, ages 40 to 75. Some participants were given a 5 mg daily dose of rosuvastatin, a statin that is sold under the brand name Crestor for 28 days. Others were given supplements, including fish oil, cinnamon, garlic, turmeric, plant sterols or red yeast rice for the same period.
The maker of Crestor, Astra Zeneca sponsored the study, but the researchers worked independently to design the study and run the statistical analysis.
“What we found was that rosuvastatin lowered LDL cholesterol by almost 38% and that was vastly superior to placebo and any of the six supplements studied in the trial,” study author Luke Laffin, M.D. of the Cleveland Clinic’s Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute told NPR. He says this level of reduction is enough to lower the risk of heart attacks and strokes. The findings are published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Oftentimes these supplements are marketed as ‘natural ways’ to lower your cholesterol,” says Laffin. But he says none of the dietary supplements demonstrated any significant decrease in LDL cholesterol compared with a placebo. LDL cholesterol is considered the ‘bad cholesterol’ because it can contribute to plaque build-up in the artery walls – which can narrow the arteries, and set the stage for heart attacks and strokes.
“Clearly, statins do what they’re intended to do,” the study’s senior author Steve Nissen, M.D., a cardiologist and Chief Academic Officer of the Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute at Cleveland Clinic told NPR.
Forbes informs us
In healthcare contexts, American consumers have historically tended to abandon their consumerism skills, often entering the doctor’s office or insurance process helpless, overwhelmed, and at the mercy of the system. Even when consumers have high expectations for their healthcare experiences, they’re often disappointed.
New research suggests that those days may be over. According to the 2022 Patient Access Journey Report, released last week from Kyruus, “Patients are consumers first.”
For the sixth year in a row, Kyruus has surveyed 1,000 consumers across geographies and generations to understand their preferences for selecting and accessing healthcare services. This year’s report focuses on three aspects of the healthcare consumer experience: search, selection, and action.
The latest findings suggest consumers, in fact, now weigh similar factors in choosing their healthcare providers and service sites as they do with other types of services. * * *
Healthcare provider websites have a two-to-one advantage in consumer trust compared with health insurance sites. Forty-four percent of consumers surveyed said that they view healthcare provider websites as the most trustworthy source for information about healthcare providers or services, compared with 20% who rated health insurance providers as the most trustworthy. But the percentage of respondents who said health insurance providers were the most trustworthy sources of information jumped nine points since 2021.
From the miscellany department
- NPR Shots explains what to watch for in the RSV surge and answers about treatment options
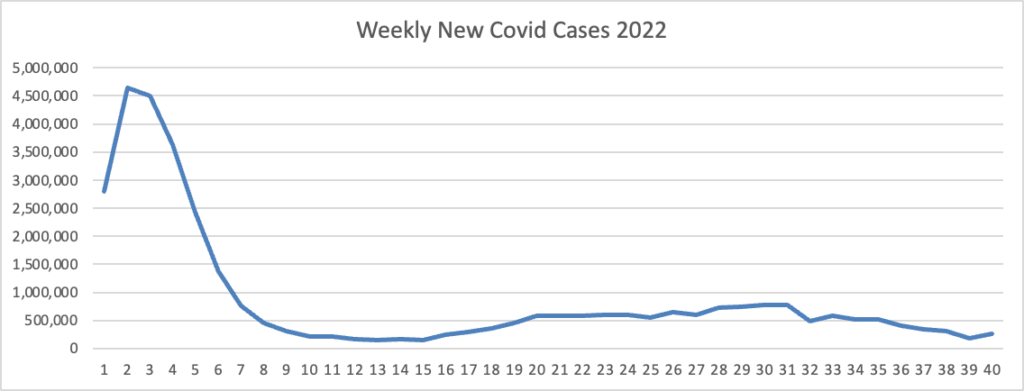
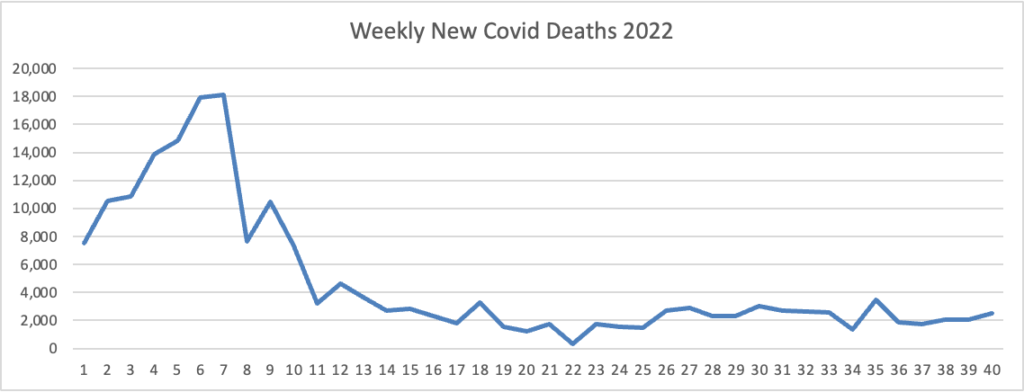
- MedPage Today calls our attention to models leading to a favorable Covid conclusion
The U.S. probably won’t see a major surge in COVID deaths this winter, according to new models from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington in Seattle.
By Feb. 1, 2023, daily deaths are projected to be at a high point of 335, which pales in comparison to the approximate 2,500 daily deaths seen during the Omicron surge around the same time last year, according to a recently published IHME policy brief.
- The Wall Street Journal discusses the Menty B (mental breakdown) hashtag in use in Instagram and Tik Tok and a boarding high school in Massachusetts which replaced their students smart phones with light phones. The school also banned teachers from using smart phones while teaching. Everyone’s happier.