Midweek Update

From Capitol Hill, Fierce Healthcare tells us
The House unanimously passed the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act on Wednesday via a voice vote. The legislation, which has new transparency requirements for MA plans, now heads to the Senate.
Lawmakers behind the legislation said in a joint statement the bill will “make it easier for seniors to get the care they need by cutting unnecessary red tape in the healthcare system,” said Reps. Suzan DelBene, D-Washington, Mike Kelly, R-Pennsylvania, Ami Bera, M.D., D-California, and Larry Bucshon, M.D., R-Indiana.
It’s worth noting that traditional Medicare has no prior authorization requirements. Beckers Payer Issues adds
Enrollees in Medicare Advantage were less likely to receive low-value care than those enrolled in traditional Medicare, a new study published in JAMA Open Network found.
The study, published Sept. 9, found Medicare Advantage enrollees received 9.2 percent fewer low-value services than their counterparts using traditional Medicare.
Low-value care is services that provide little clinical benefit or cause more harm than benefits for a patient.
The study’s authors, lead by researchers from Humana and Boston-based Tufts University School of Medicine, compared enrollees in a large, national Medicare Advantage plan to a random sample of 5 percent of traditional Medicare beneficiaries.
The study found among Medicare Advantage enrollees, those who had HMO plans were less likely to receive low-value care than those with PPO plans.
Read the full study here.
Hopefully, Congress will not throw out the baby with the bath water.
From the federal employee benefits front, FedWeek informs us
OPM has issued a reminder to agencies of their authority to verify that family members being covered under the FEHB actually are eligible, including the process to be used and the documentation required.
The notice calls attention to a revision of the FEHB handbook section on family member eligibility reflecting several instructions of recent years, including one telling agencies to tighten scrutiny of those covered and another laying out procedures for removing those deemed ineligible. That is a response to several inspector general reports warning that ineligible persons are being insured under the program, raising premium costs to the government and to other FEHB enrollees.
That directive, now part of the handbook, lists agency responsibilities to verify eligibility of family members during initial enrollment of newly hired employees and when family members are being added to an existing enrollment due to a “qualifying life event” such as marriage.
In the middle of the last decade, OPM added a standard contract provision to FEHB contract requiring carriers to share the cost of any family member eligibility audit that OPM undertakes. OPM has not yet exercised that provision.
It turns out that for the past two weeks federal employee benefits expert Reg Jones has been writing in Fedweek about federal employee retirement benefits. Today’s he discusses survivor benefits which includes a squib about perhaps the most unique and valuable survivor benefit — FEHB coverage for the survivor’s life with the full government contribution as explained here:
If your spouse receives a survivor annuity and was covered under either the Self Plus One or Self and Family option of your Federal Employees Health Benefits plan when you died, he or she and all eligible children can continue that coverage. If the annuity amount is less than the premiums required, your spouse will be able to make payments directly to OPM to cover the cost.
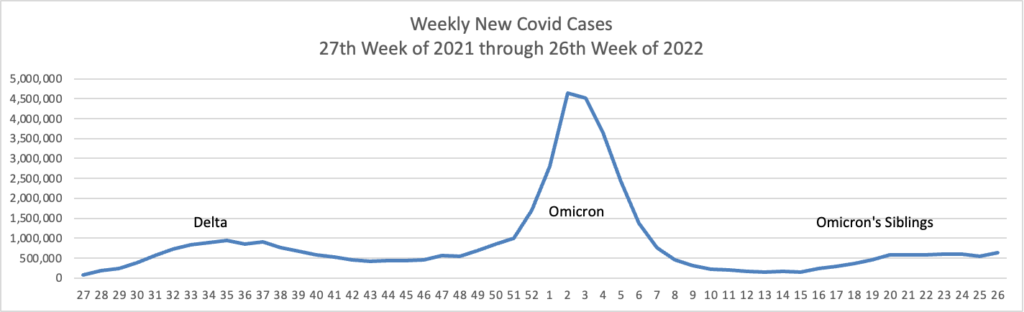
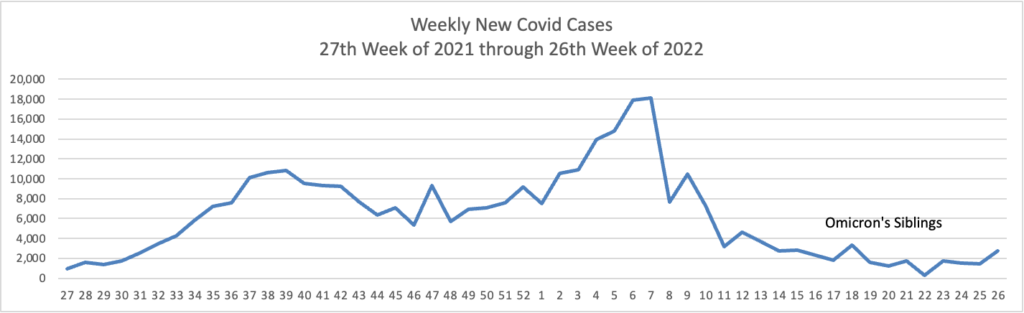
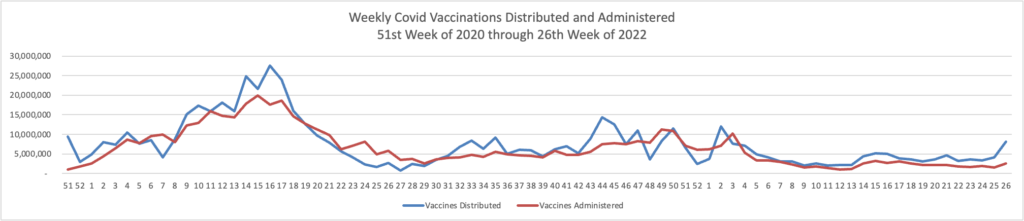
From the Omicron and siblings front, we have two thoughtful pieces from MedPage Today
In other virus news, the American Hospital Association reports
The recent paralytic polio case in an unvaccinated adult in Rockland County, N.Y. and wastewater samples from communities near the patient’s residence meet the World Health Organization’s criteria for circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced yesterday. Genetic sequences from the virus in the patient and wastewater specimens have been linked to wastewater samples in Jerusalem and London, indicating community transmission, CDC said.
Thirty other countries have circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus, which is not caused by the polio vaccine but occurs when local immunity to poliovirus is low enough to allow prolonged transmission of the original weakened virus in the oral polio vaccine. Oral polio vaccine has not been used or licensed in the U.S. since 2000 but continues to be used in some countries. N.Y. Governor Kathy Hochul last week declared a state of emergency to help expand vaccination efforts and surveillance.
“Polio vaccination is the safest and best way to fight this debilitating disease and it is imperative that people in these communities who are unvaccinated get up to date on polio vaccination right away,” said Dr. José R. Romero, director of CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. “We cannot emphasize enough that polio is a dangerous disease for which there is no cure.”
From the No Suprises Act front, Beckers Hospital CFO Report relates
The No Surprises Act, which prevents patients from receiving surprise bills from out-of-network providers at emergency rooms, could lead to an increase in emergency department visits, a new study from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality found.
The study, published Sept. 12 in The American Journal of Medical Care, compared emergency department visits rates in 15 states that implemented bans on balance billing between 2007 and 2018 to rates in 16 states where these bills were not banned.
The study’s authors found that state-level bans reduced spending per emergency room visit by 14 percent but increased emergency room visits by 3 percentage points. These visits were 9 percent less urgent than before the balance billing ban, according to an emergency department severity index.
Based on the state-level analysis, the study’s authors, led by AHRQ researcher William Encinosa, PhD, conclude that the No Surprises Act, which took effect this year, could result in 3.5 million more emergency room visits annually.
“Because individuals will no longer have the fear of a possible catastrophic surprise ED bill not covered by their insurer, they may be more inclined to go to the ED in marginal, less severe cases,” the authors wrote.
Read the full study here.
In the FEHBlog’s opinion, the No Surprises Act is working well, and he does not foresee a surge in ER visits because going to the emergency room is no picnic.
In preventive services news, MedPage Today reports
The jury is still out on whether asymptomatic children and adolescents should be screened for diabetes, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) said.
In a new recommendation statement published in JAMA, the task force concluded that there is insufficient evidence to weigh the benefits and harms of screening for type 2 diabetes in this pediatric population, despite rising rates of disease.
“[T]here is inadequate evidence that screening and early intervention lead to improvements in health outcomes such as renal impairment, cardiovascular morbidity, mortality, and quality of life,” wrote Carol M. Mangione, MD, MSPH, of the University of California Los Angeles, and colleagues.
From the miscellany department —
- The Department of Health and Human Services announced that today HHS “Secretary Xavier Becerra formally swore in Melanie Fontes Rainer as Director of the Office for Civil Rights (OCR). Director Fontes Rainer previously served as the Acting Director and was officially appointed to the role last month. OCR is responsible for enforcing federal civil rights; conscience protections; the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Privacy, Security, and Breach Notification Rules; and the Patient Safety and Quality Improvement Act and Patient Safety Rule – which together protect individuals’ fundamental civil rights and medical privacy.”
- The Justice Department announced “the establishment of three Strike Force teams created to enhance the Department’s existing efforts to combat and prevent COVID-19 related fraud. “These Strike Force teams will build on the Department’s historic enforcement efforts to deter, detect, and disrupt pandemic fraud wherever it occurs,” said Attorney General Merrick B. Garland. “Since the start of this pandemic, the Justice Department has seized over $1.2 billion in relief funds that criminals were attempting to steal, and charged over 1,500 defendants with crimes in federal districts across the country, but our work is far from over. The Department will continue to work relentlessly to combat pandemic fraud and hold accountable those who perpetrate it.” The Strike Force teams will operate out of U.S. Attorney’s Offices in the Southern District of Florida, the District of Maryland, and a joint effort between the Central and Eastern Districts of California.”
- Please check out this STAT News investigation
The good news is there’s a cure for hepatitis C. The bad news is how hard it is to bring that miracle cure to the people who need it. For years experts assumed the drug’s astronomical price was the biggest barrier. So in 2019, Louisiana and Washington state adopted the “Netflix model,” as in paying a lower price for abundant access to the drug. Just last week the White House jumped on board for a national version.
But STAT’s Nicholas Florko has found that neither state is near its goal. In Washington, the treatment rate for Medicaid patients is now lower than before the initiative began, even with a lower price. “The further you get out in the population … the more you start to hit this population that is harder — harder to identify, more costly to convert to treatment,” Rena Conti of Boston University told Nick. Read his investigation here.
- The National Institute of Health’s HEAL Program offers ways to build opioid use disorder prevention into everyday life.
- Govexec discusses OPM’s efforts to “highlight ways federal employees can contribute to the White House’s fight against hunger and to improve Americans’ health and nutrition, including through an event later this month.”