Thursday Miscellany

From Capitol Hill, the American Hospital Association reports
The Senate today voted 72-25 to pass and send to the House a continuing resolution that would extend current federal funding levels for health care and other programs through Dec. 16. Current government funding expires at midnight Sept. 30.
The legislation also would extend through Dec. 16 two expiring programs that help maintain access to care in rural communities: the Medicare-dependent Hospital and enhanced Low-volume Adjustment programs. AHA will continue to advocate for long-term extension of these programs. Among other provisions, the continuing resolution would reauthorize the Food and Drug Administration’s user fee programs, and provide emergency funding for Ukraine and disaster assistance.
A proposal dealing with energy-permitting plans was dropped from the measure on Tuesday, speeding passage of the legislation. The House is expected to pass the measure by Friday.
Roll Call provides more background on the CR.
The American Hospital Association also tells us
The House voted 220-205 today to pass legislation to hold employer-based health plans more accountable for improper denials of mental health and substance use benefits. The Mental Health Matters Act (H.R.7780) would give the Department of Labor more authority to enforce plan requirements under the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act and Employee Retirement Income Security Act, ban forced arbitration agreements when plans improperly deny benefits and ensure a fair standard of review by the courts. The bill also would provide grants to develop, recruit and retain school-based mental health professionals and link schools with local mental health systems, among other provisions.
Fierce Healthcare provides more color on this troubling bill.
The ERISA Industry Committee (ERIC)—which represents large employer plan sponsors—wrote a letter Monday to all House members calling for them to oppose (PDF) the Mental Health Matters Act when it comes up for a vote later this week. The letter comes as Congress is considering how to improve pay parity between behavioral and physical health amid reports of some insurers not following requirements in the Affordable Care Act.
“This bill includes provisions that weaponize the Department of Labor (DOL) to sue employers rather than helping them come into compliance,” the letter said. * * *
[I]t remains unclear whether the Senate will take it up. The Senate Finance Committee is considering action to tackle pay parity but so far has not released any legislation. Chairman Ron Wyden, D-Oregon, previously told Fierce Healthcare that he is still working on legislation to tackle the issue, including taking aim at “ghost networks” where providers listed in directories don’t take new patients.
Earlier this month, Healthcare Dive reported that
The Senate Finance Committee released a bipartisan-supported discussion draft bill that aims to increase mental health access and improve mental health workforce shortages.
The draft bill proposes to fill the gap in mental healthcare worker shortages by funding training for 400 additional Medicare Graduate Medical Education psychiatric slots for residencies per year beginning Oct. 1, 2024. Over a decade, 4,000 psychiatric residencies would be supported by the funding, according to the bill.
The Senate’s focus on access to care makes much more sense than the House’s punitive approach, particularly considering the unnecessary complexity of the federal mental health parity law.
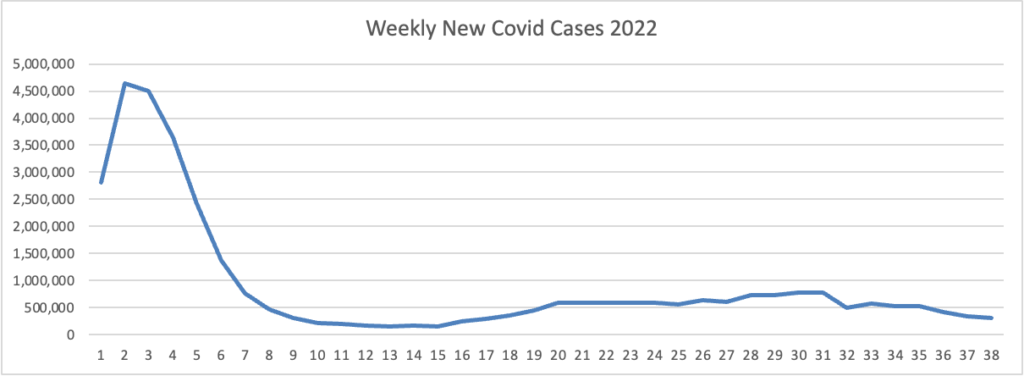
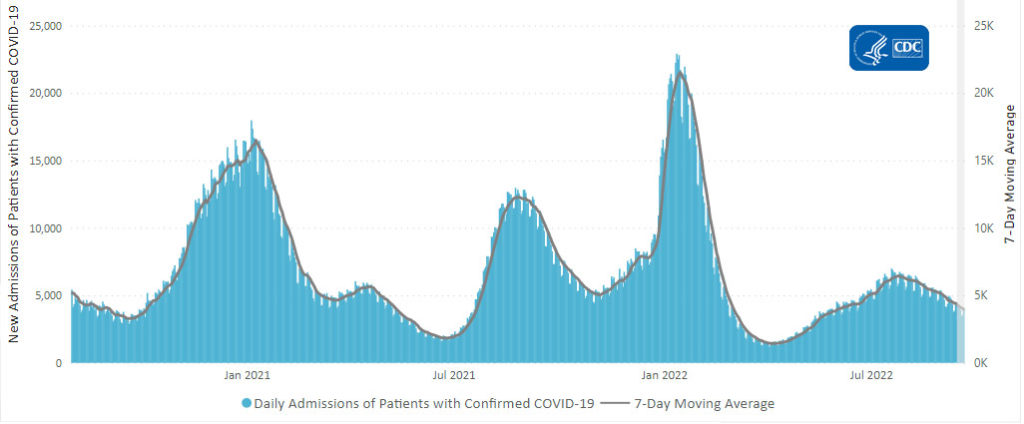
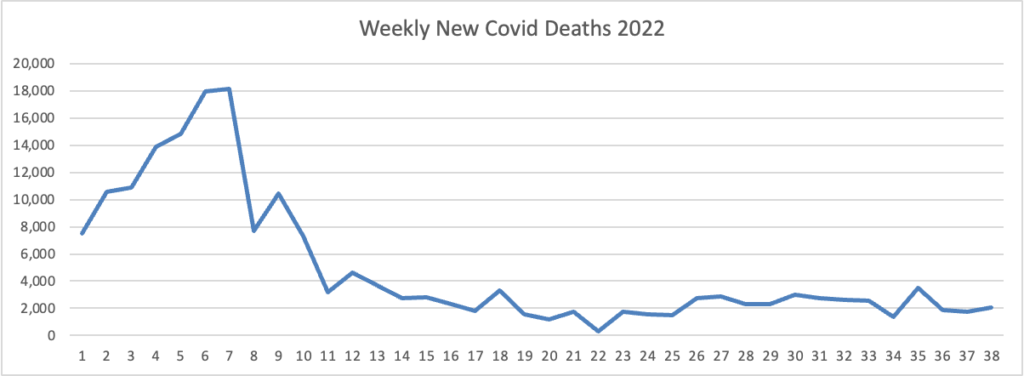
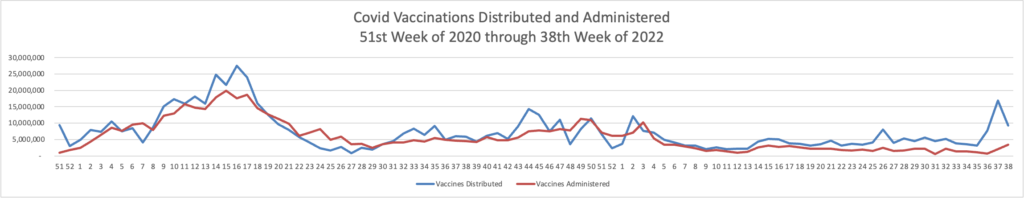
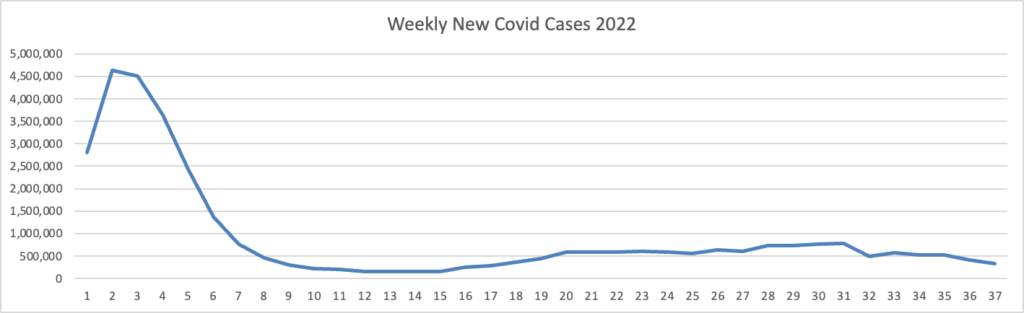
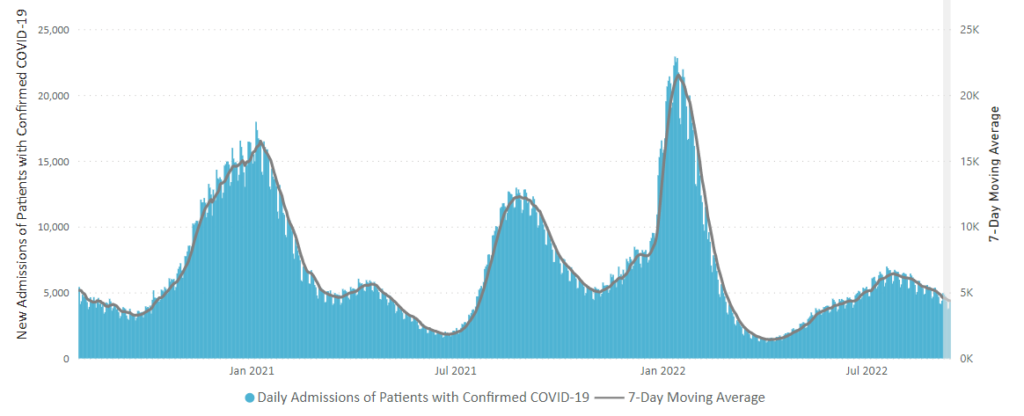
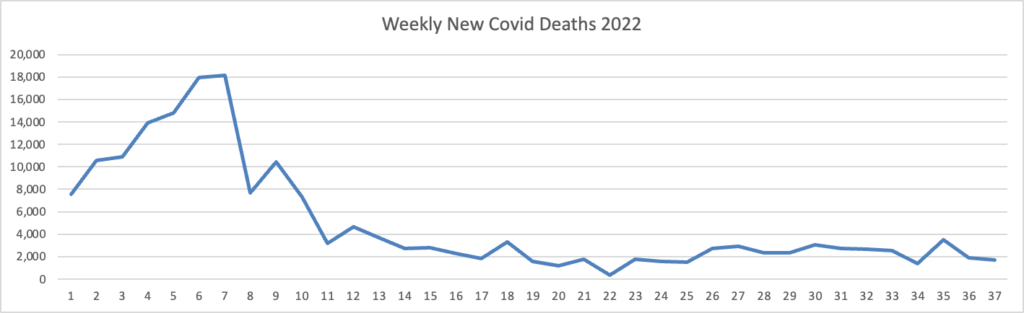
From the Omicron and siblings front, MedPage Today discusses nasally administered Covid vaccines now under development. “The idea is that mucosal vaccines could bolster immunity at these viral entry points, stopping the pathogen from implanting, multiplying, and transporting itself throughout the body.” Finger crossed.
From the monkeypox front, CNBC reports
A single dose of the two-dose monkeypox vaccine provides some protection against the virus, according to CDC data.
People at risk of monkeypox who have not received a shot are 14 times more likely to get infected, the preliminary data found.
These are the first real-world findings on how well the vaccine is working in the current outbreak.
The CDC is still recommending that everyone at risk receive two doses of the vaccine.
From the Food and Drug Administration front —
STAT News informs us
The Food and Drug Administration approved a new medicine for ALS from Amylyx Pharmaceuticals on Thursday, providing a desperately-needed new treatment option for a devastating disease.
The medicine, to be sold as Relyvrio, is not a cure for ALS but proved to moderately slow the progression of the neurological disease, which causes the destruction of neurons in the brain and spinal cord, resulting in weakened muscles, paralysis, and death.
Amylyx did not immediately disclose how much it will charge for Relyvrio. “Amylyx’s goal is that every person who is eligible for Relyvrio will have access as quickly and efficiently as possible,” the company’s co-CEOs said in a statement, “as we know people with ALS and their families have no time to wait.”
Healio relates
The FDA approved bevacizumab-adcd for the treatment of six cancer types, according to a press release from the biosimilar’s manufacturer.
Bevacizumab-adcd (Vegzelma, Celltrion USA), a biosimilar to bevacizumab (Avastin, Genentech), is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and prohibits it from binding to VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 on the surface of endothelial cells.
FDA approved bevacizumab-adcd for metastatic colorectal cancer; recurrent or metastatic nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer; metastatic renal cell carcinoma; recurrent glioblastoma; persistent, recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer; and epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube or primary peritoneal cancer.
In medical research news, STAT News tells us
After a steep drop in its stock price and with mounting competition from rivals, genomics giant Illumina on Thursday launched a new line of high-powered DNA sequencers, ratcheting up the race to read genetic information accurately and cheaply.
The new instruments, dubbed the NovaSeq X Series, can churn out up to 20,000 human genomes in a year, 2.5 times the max output of the company’s current machines, executives announced. The cost of generating this data has dropped, too, from about $5 per billion DNA bases on Illumina’s last line of high-end sequencers to as low as $2 on the new products.
That will bring the cost of reading a whole human genome on the company’s equipment from about $600 to $200, which could help make sequencing more mainstream in everyday medicine. While the price of sequencing isn’t the only obstacle to using genomics to improve human health, it remains a major factor.
Intriguing.
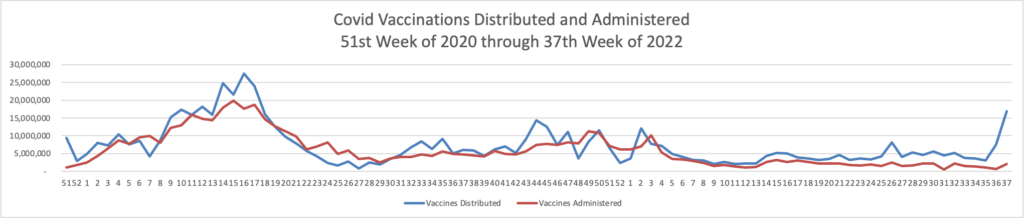
From the Medicare front, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) announced 2023 Medicare Advantage plan and Part D prescription drug plan premiums in advance of the Medicare Open Enrollment, which runs from October 15 through December 7, 2022.
The projected average premium for 2023 Medicare Advantage plans is $18 per month, a decline of nearly 8% from the 2022 average premium of $19.52. Medicare Advantage plans will continue to offer a wide range of supplemental benefits in 2023, including eyewear, hearing aids, preventive and comprehensive dental benefits, access to meals (for a limited duration), over-the-counter items, and fitness benefits.
[T]he average basic monthly premium for standard Part D coverage is projected to be $31.50, compared to $32.08 in 2022.
To view the premiums and costs of 2023 Medicare Advantage and Part D plans, please visit: https://www.cms.gov/medicare/prescription-drug-coverage/prescriptiondrugcovgenin. Select the various 2023 landscape source files in the downloads section of the webpage.
For state-by-state information, important dates and enrollment resources for Medicare Advantage and Part D in 2023, please visit: https://www.cms.gov/files/document/2023-medicare-advantage-and-part-d-state-state-fact-sheets.pdf
For more information on the Medicare Advantage Value-Based Insurance Design Model, including plan participation, please visit: https://innovation.cms.gov/innovation-models/vbid.
From the telehealth front, the Wall Street Journal reports a tragic story —
Cerebral treated a 17-Year-Old without His parents’ consent. They found out the day he died.
Telehealth startup didn’t use software to flag minors, according to employees and documents; company says it complies with state rules and the case is an outlier.Anthony Kroll signed up for Cerebral in December and uploaded his Missouri intermediate driver’s license showing he was 17. Missouri law prohibits clinicians from providing mental-health treatment to people under 18 without parental consent.
Anthony told a Cerebral clinician he had suicidal thoughts, and she prescribed him an antidepressant that carries a warning label for adolescents, according to medical records reviewed by the Journal. Cerebral didn’t notify his family.
His parents, Wendi and Todd Kroll, said they didn’t know their son was suicidal or was seeking mental-health treatment. “I had no idea he was even on [medication] until the day he died,” Mrs. Kroll said, adding that she found the pill bottle at their home a few hours before her son died by suicide.
A Cerebral spokesman said Anthony misrepresented his age, the company regrets he received care without parental consent, and the treatment he received was appropriate. “This case is an unfortunate outlier,” the spokesman said. “Any loss of life is tragic, and we extend our deepest condolences to the family.”
From the miscellany department
- The GAO released a report titled “Artificial Intelligence in Health Care: Benefits and Challenges of Machine Learning Technologies for Medical Diagnostics.” ” Machine learning technologies can help identify hidden or complex patterns in diagnostic data to detect diseases earlier and improve treatments. We identified such technologies in use and development, including some that improve their own accuracy by learning from new data. But developing and adopting these technologies has challenges, such as the need to demonstrate real-world performance in diverse clinical settings.”
- Federal News Network tells us
Agencies may soon get some more specific guidance on how best to implement President Joe Biden’s sweeping executive order on diversity, equity, inclusion and accessibility in the federal workforce.
The Chief Diversity Officers Executive Council, a governmentwide panel composed of agencies’ chief diversity officers and led by the Office of Personnel Management, held its first-ever meeting on Sept. 29.
“This has been a really long time coming,” OPM Director Kiran Ahuja said in an exclusive interview with Federal News Network.