Tuesday Tidbits

Happy Mardi Gras!
As the FEHBlog has noted, the FEHB Program has unique demographics compared to other employer sponsored health plans because the federal government offers generous FEHB annuitant coverage to its employees. FEHB enrollment is roughly 52% active employees and 48% annuitants. The average age of federal and postal employees is late forties and the FEHBlog understands that average age of an FEHB enrollee is sixty. (OPM offers detailed demographic statistics on its workforce but not on its retirement system members. No complaints, just stating a fact.)
Today HHS’s Agency of Healthcare Research and Quality issued a fascinating report titled “Concentration of Healthcare Expenditures and Selected Characteristics of High Spenders, U.S. Civilian Noninstitutionalized Population, 2018.” Here are the report’s highlights:
- In 2018, the top 1 percent of persons ranked by their healthcare expenditures accounted for about 21 percent of total healthcare expenditures, while the bottom 50 percent accounted for only about 3 percent.
- Persons ages 65 and older and whites were disproportionately represented in the top spending tiers.
- Inpatient hospital care accounted for 36 percent of spending for persons in the top 5 percent of the spending distribution.
- About three-quarters of aggregate expenses for persons in the top 5 percent of spenders were paid for by private insurance or Medicare.
In 2018, the top 1 percent of persons ranked by their healthcare expenditures accounted for 21 percent of total healthcare expenditures (100 minus 79 percent; figure 1), with an annual mean expenditure of $127,284 (figure 2). The group within the top 1 percent is defined as persons who spent $72,212 or more during the year. Cut points for additional percentile groups are shown in table 1 [immediately below]. The top 5 percent of the population accounted for 48.3 percent of total expenditures (100 minus 51.7 percent), with an annual mean expenditure of $58,609. The bottom 50 percent accounted for only 3.2 percent of total healthcare expenditures. Every person in this group spent less than $1,317 during the year (table 1), with an average annual expenditure of $384 (figure 2).
| Percentile of population | 2018 Expenditure |
|---|---|
| Top 1% | $72,212 or more |
| Top 5% | $26,355 or more |
| Top 10% | $14,651 or more |
| Top 30% | $3,776 or more |
| Bottom 50% | Less than $1,317 |
But given the FEHB’s demographics, this figure particularly caught the FEHBlog’s eye:
Figure 4: Percentage of persons by age group and percentile of spending, 2018
| Age group | Overall percentage | Bottom 50% | Top 50% | Top 10% | Top 5% |
| 0–17 | 22.6 | 30.6 | 14.5 | 6.4 | 5.8 |
| 18–44 | 35.2 | 43.2 | 27.3 | 20.8 | 18.9 |
| 45–64 | 25.4 | 20.1 | 30.7 | 33.4 | 36.3 |
| 65+ | 16.8 | 6.0 | 27.5 | 39.4 | 39.0 |
It is a credit to OPM and the FEHB carriers that they are able to hold premiums rather stable.
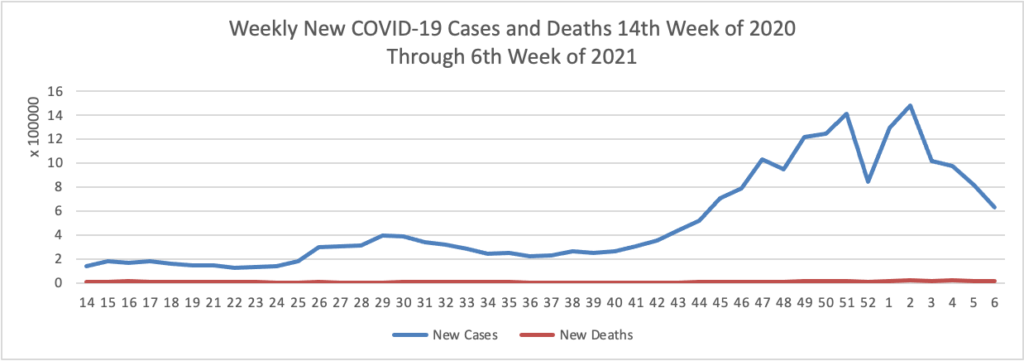
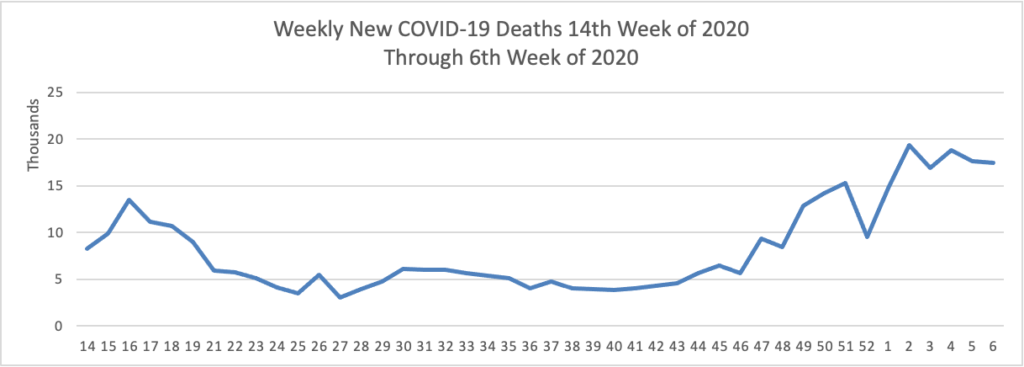
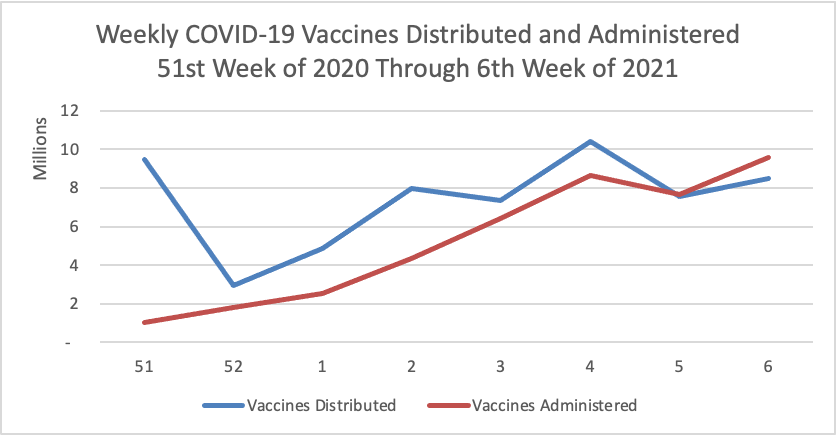
On the COVID-19 vaccination front —
- NPR updates us with encouraging COVID-19 vaccination distribution statistics.
- Federal News Network tells us that “The Biden administration’s Safer Federal Workforce Task Force has new details on how agencies should handle [COVID-19 vaccination] leave, labor unions and mask mandates during the ongoing pandemic.”
- The Centers for Disease Control now offers guidance on how to arrange COVID-19 vaccinations for home-bound individuals.
Healthcare Dive reports on CVS Health’s fourth quarter 2020 earnings report. The headline is that CVS Health’s payer arm Aetna plans to return to the Affordable Care Act marketplace for 2022.
CVS’ fourth quarter revenue of $69.6 billion, up 4% year over year, was mostly due to growth in the benefits segment. Healthcare benefits reported quarterly revenue of $19.1 billion, up 11% year over year, driven primarily by membership growth in Medicaid and Medicare products and partially offset by a drop in commercial membership and COVID-19 costs.
As of the end of 2020, CVS covered 23.4 million lives. Despite fluctuating membership and utilization due to COVID-19 over the course of last year, overall utilization in the fourth quarter was generally back to normal, executives said. The company’s medical loss ratio, a marker of how much it’s reinvesting in patient care, was 86.7% in the quarter, compared to 85.7% same time last year.
JDSupra includes this employment law article titled “Employees Starting to Receive the COVID-19 Vaccine – Now What?” which is worth a gander in the FEHBlog’s opinion.