Friday Stats and More
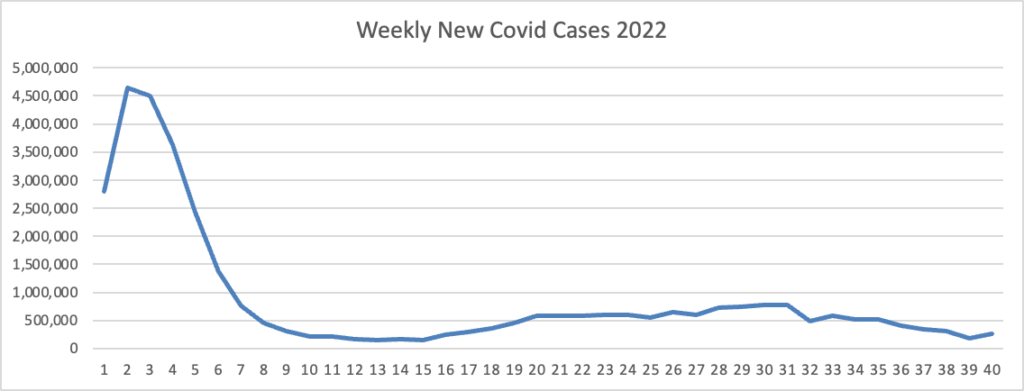
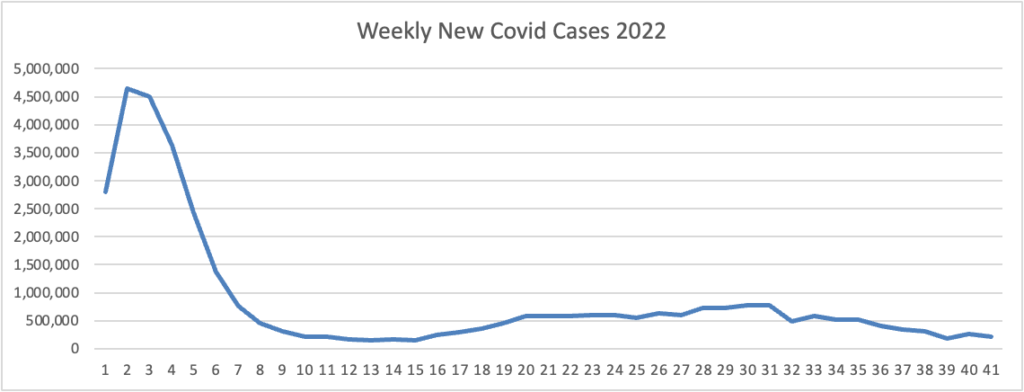
Based on the Centers for Disease Control’s Covid Data Tracker and Thursday as the first day of the week, the FEHBlog presents his weekly chart of new Covid cases for 2022.
The CDC’s weekly interpretation of its Covid statistics reports
As of October 12, 2022, the current 7-day moving average of daily new cases (38,949) decreased 11.9% compared with the previous 7-day moving average (44,233).
CDC Nowcast projections* for the week ending October 1, 2022 estimate that the combined national proportion of lineages designated as Omicron will continue to be 100%. There are eight designated as Omicron: BA.5, BA.4.6, BQ.1.1, BQ.1, BF.7, BA2.75.2, BA.2.75, and BA.4. The predominant Omicron lineage is BA.5, projected to be 67.9% (95% PI 64.1-71.4%).
The Wall Street Journal points out
New offshoots of the Omicron Covid-19 variant that virus experts say appear to spread easily are on the rise in the U.S., the latest federal data show, underscoring how the virus is mutating and presenting new risks as it proliferates.
Two of the Omicron subvariants, both related to the BA.5 version that drove the most recent U.S. surge, are called BQ.1 and BQ.1.1. They were estimated to represent a combined 11.4% of U.S. Covid-19 cases by mid-October, according to estimates the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released Friday. * * *
Virus experts said that, because the newer subvariants remain in the Omicron family, updated Covid-19 vaccines in the U.S. should be an important shield against severe illness and death, though data is limited. The bivalent shots were designed to fight the original virus strain as well as the BA.4 and BA.5 Omicron subvariants.
Here is the CDC’s “Daily Trends in Number of New COVID-19 Hospital Admissions in the United States” chart.
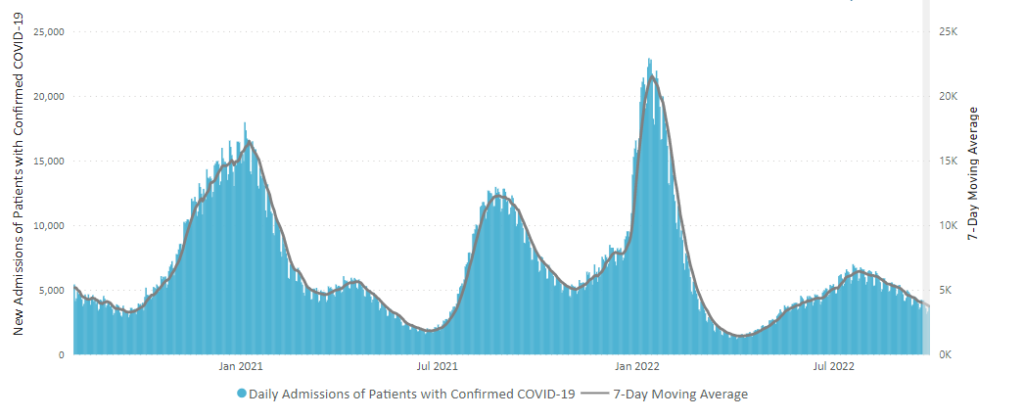
The CDC’s summary explains “The current 7-day daily average for October 5–11, 2022, was 3,268. This is a 4.4% decrease from the prior 7-day average (3,419) from September 28–October 4, 2022.”
The Wall Street Journal adds
Nationally, key metrics such as hospitalizations have largely been on a downward trajectory since late July, following a BA.5-fueled summertime surge, but with some recent signs of wavering. Wastewater virus readings have been choppy in recent weeks due to a climb in the Northeast, according to data from Biobot Analytics. The Northeast has also seen a recent rise in new Covid-19 hospital admissions, federal data show.
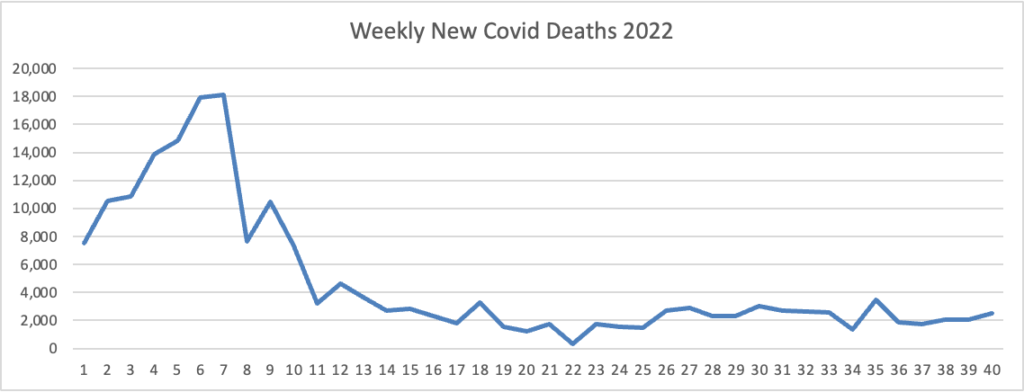
The FEHBlog presents his weekly chart of new Covid deaths for 2022
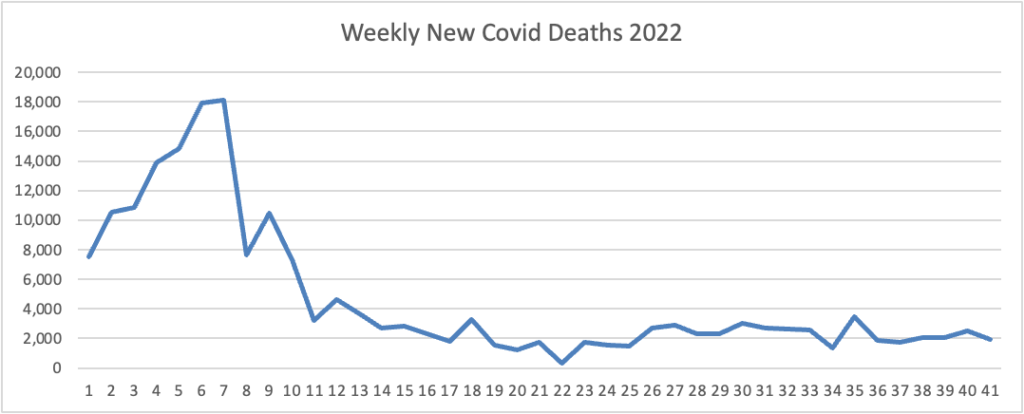
The CDC’s summary explains “The current 7-day moving average of new deaths (328) decreased 8.5% compared with the previous 7-day moving average (359).”
The Wall Street Journal adds
The country has recently averaged about 330 newly reported Covid-19 deaths each day, a continued burden falling heavily on the elderly and people with underlying health issues, including compromised immune systems. * * *
The interplay of a changing virus and fading immune protection from earlier infections and vaccine shots has left people vulnerable to repeated cases. These can lead in some cases to long-running symptoms. But virus experts say built-up protections from vaccines and prior infections still matter and can help limit hospitalizations and deaths.
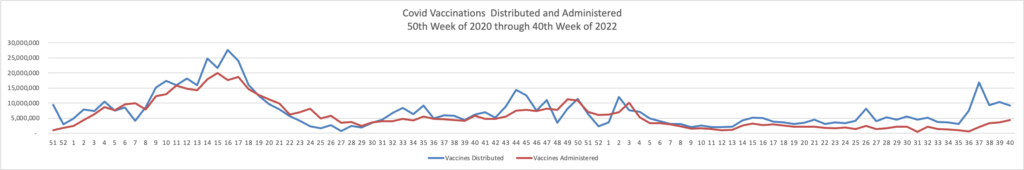
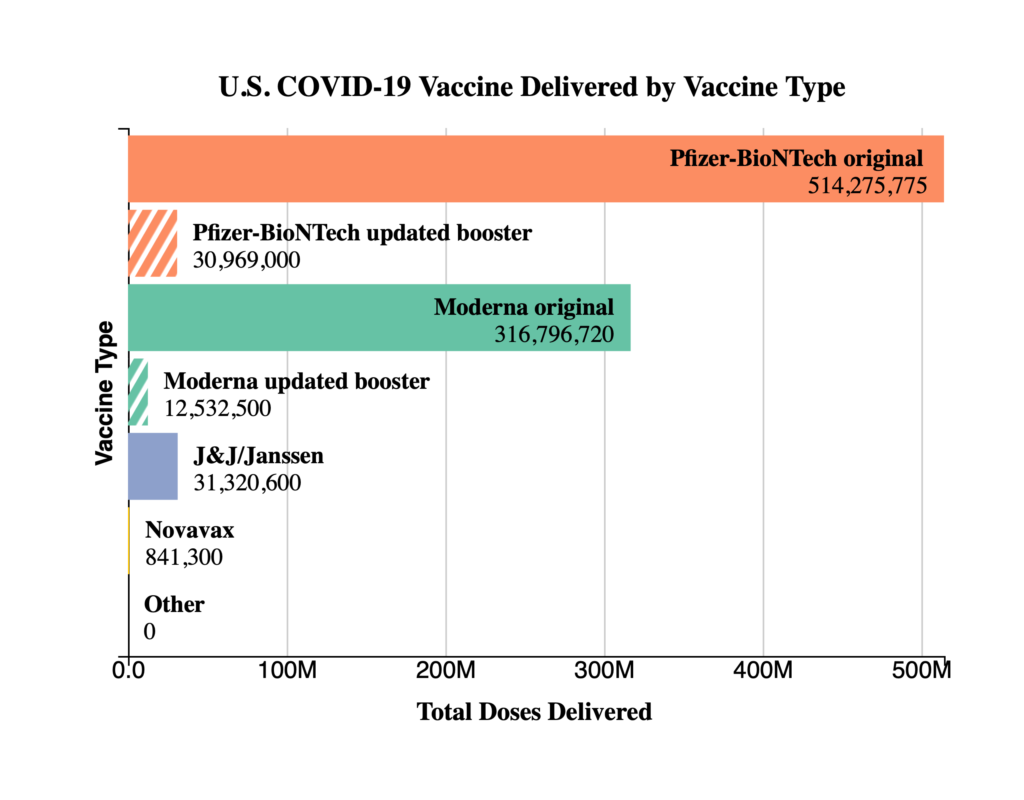
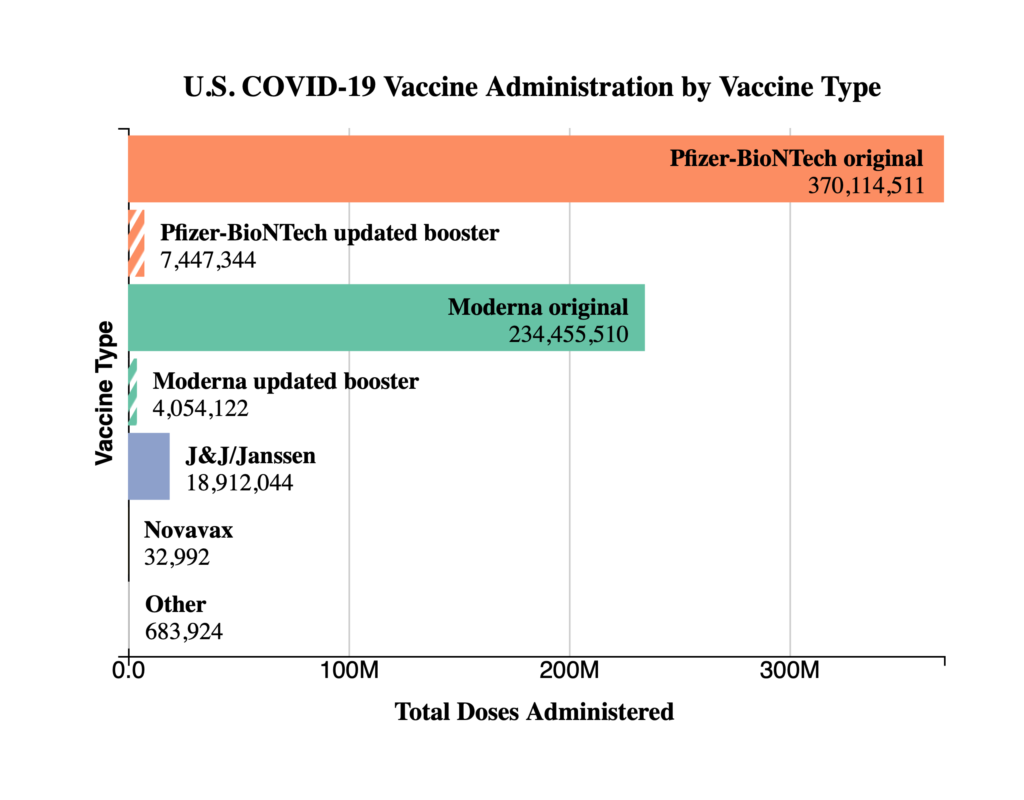
The FEHBlog presents his weekly chart of Covid vaccinations distributed and administered from the beginning of the Covid vaccination era in December 2020 through the 41st week of 2022:
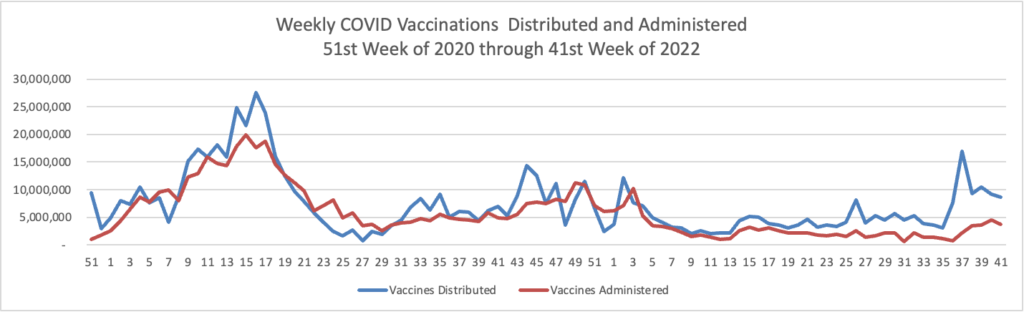
The CDC’s summary explains
As of October 12, 2022, 627.9 million vaccine doses have been administered in the United States. Overall, about 265.1 million people, or 79.9% of the total U.S. population, have received at least one dose of vaccine. About 226.2 million people, or 68.1% of the total U.S. population, have completed a primary series.
It strikes the FEHBlog as odd that the CDC’s Covid daily reporting does not include dispensing of oral antiviral drugs for Covid treatment, a vital component of the Covid suppression strategy.
Yesterday, the Secretary of Health and Human Services renewed the Covid public health emergency for another 90 days. The American Hospital Association comments
The AHA had urged HHS to renew the public health emergency to continue critical flexibilities hospitals depend on to deliver needed care, and minimize additional disruptions to an “increasingly fragile” health care delivery system.
From the U.S. healthcare business front, Healthcare Dive reports
UnitedHealth beat Wall Street expectations on both earnings and revenue in the third quarter with revenue of $80.9 billion, up 12% year over year. The healthcare giant increased its 2022 earnings expectations as a result.
Minnetonka, Minnesota-based UnitedHealth chalked the rise up to an increase in members served by payer UnitedHealthcare and growth in value-based care arrangements and care delivery platforms at Optum. Both businesses reported double-digit growth.
On a call with investors Friday morning, CFO John Rex said that UnitedHealth expects Change Healthcare — the data analytics business UnitedHealth acquired earlier this month despite a challenge from regulators — to be accretive to Optum’s earnings next year, not in 2022 as previously expected.
From the FEHB front
- GEHA issued a press release on its 2023 FEHB benefit changes.
- Kaiser Health News reports on a “New Generation of Weight Loss Medications Offer Promise — But at a Price.” FEHB plan enrollees will find expanded coverage of the drugs for 2023 due to a sensible OPM requirement in the 2023 call letter.
In other open season news, the Department of Health and Human Services issued a press release on the Medicare Open Enrollment period, which begins on Saturday, October 15.